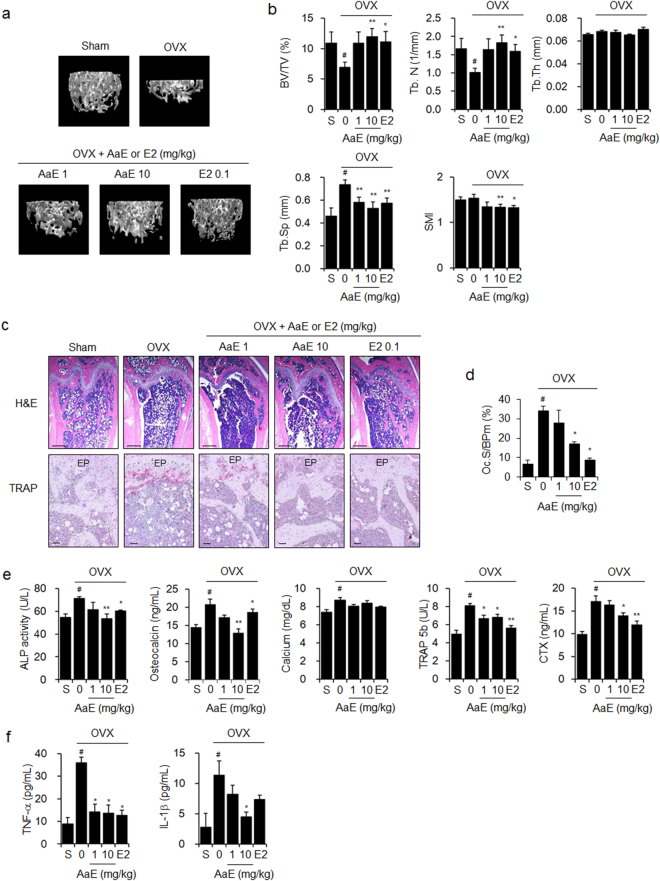
Figure 1.
AaE inhibits OVX-induced bone loss in mice. Eight-week-old female OVX mice (N = 10) were administered vehicle (PBS containing 1% DMSO and 1% Tween-20), 1 or 10 mg/kg BW of AaE, or 0.1 mg/kg BW of E2 by oral gavage 5 times per week for 12 weeks. Sham-operated mice (N = 10) received the vehicle alone. (a) The trabecular bones of the distal femora of mice were scanned using μCT at 12 weeks, and 3D images were obtained as described in the Methods section. One representative image is shown per group. (b) Bone morphometric parameters of the mouse femora, including BV/TV, Tb.N, Tb.Th, Tb.Sp, and SMI, were measured using μCT. (c) H&E and TRAP staining were performed in the sectioned femoral tissues. EP: epiphyseal plate. Scale bar: 0.396 mm for H&E staining and 10 μm for TRAP staining. (d) Osteoclast surface per bone perimeter (Oc.S/BPm) values were calculated from TRAP-stained femoral sections. (e) Serum levels of bone turnover markers and (f) the pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-1β were quantified using their respective assay kits as described in the Methods section. The data are expressed as the mean ± SE. # P < 0.01 versus sham-operated mice (S), * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01 versus OVX mice.