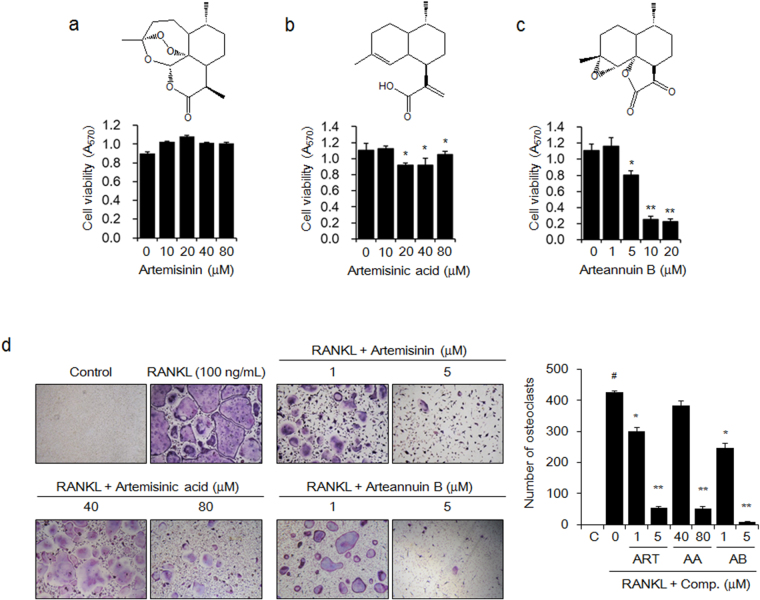
Figure 4.
The active components of A. annua attenuate RANKL-induced osteoclast formation. The BMMs were cultured with M-CSF (30 ng/mL) and the indicated concentrations of (a) artemisinin (ART), (b) artemisinic acid (AA), or (c) arteannuin B (AB) for 5 days. Cell viability was determined using an MTT assay. The data are expressed as the mean ± SE. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01 versus BMMs without active components. (d) BMMs were incubated in media with M-CSF (30 ng/mL), RANKL (100 ng/mL), and the indicated concentration of ART, AA, or AB for 5 days. Mature osteoclasts were detected by TRAP staining and TRAP-positive multinucleated cells were counted using light microscopy (magnification, ×100). The images are representative, and the data are expressed as the mean ± SE of triplicate experiments. # P < 0.01 versus BMMs without RANKL (C), * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01 versus BMMs with RANKL alone.