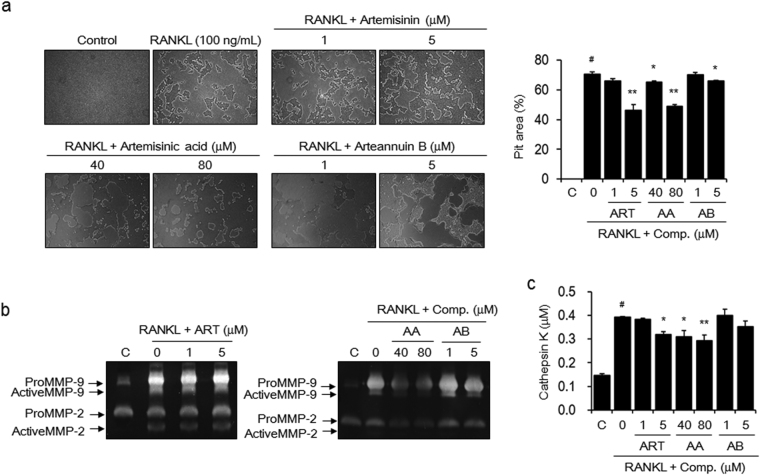
Figure 5.
The active components inhibit the activity of RANKL-induced osteoclasts. BMMs were seeded onto Osteo Assay Surface Plates and incubated in α-MEM containing M-CSF (30 ng/mL) and RANKL (100 ng/mL) for 5 days. The cells were then exposed to the indicated concentrations of artemisinin (ART), artemisinic acid (AA), or arteannuin B (AB) for an additional 2 days. (a) The cells were lysed with 5% sodium hypochlorite solution, and the formed resorption pits were examined using light microscopy (magnification, ×100). The resorbed area was calculated using ImageJ software. (b) MMP-2 and MMP-9 activities and (c) cathepsin K activity were detected using gelatin zymography and a commercially available cathepsin K assay kit. The images are representative, and the data are expressed as the mean ± SE of triplicate experiments. # P < 0.01 versus BMMs without RANKL (C), * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01 versus BMMs with RANKL alone.