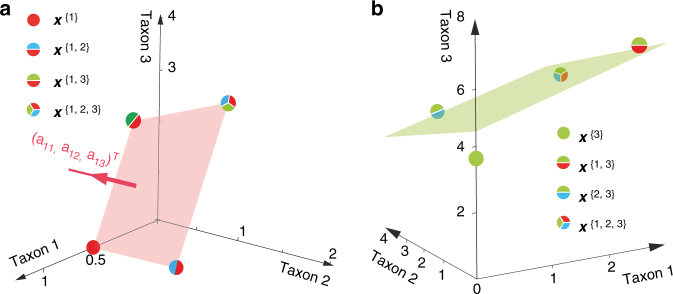
Fig. 2.
Consistency check of the GLV model and the observed steady-state samples. For a microbial community following exactly the GLV dynamics, all its steady-state samples sharing one common taxon will align onto a hyperplane in the state space. a Here we consider a microbial community of three taxa. There are four steady-state samples {} that share common taxon 1. Those four steady-state samples represent four points in the state space, and they align onto a plane (light red). The normal vector of this plane is parallel to the first row a 1 of the interaction matrix A in the GLV model. Given any one of non-zero entries in a 1, we can determine the exact values of all other entries. Otherwise, we can always express the inter-taxa interaction strengths a ij () as a function of the intra-taxa interaction strength a ii. b Here we again consider a microbial community of three taxa. Taxon-1 and taxon-2 follow the GLV dynamics, but taxon-3 does not. Then those steady-state samples that share taxon-3 do not align onto a plane anymore. Here we show the best fitted plane (in green) by minimizing the distance between this plane and the four steady states, with the coefficient of determination