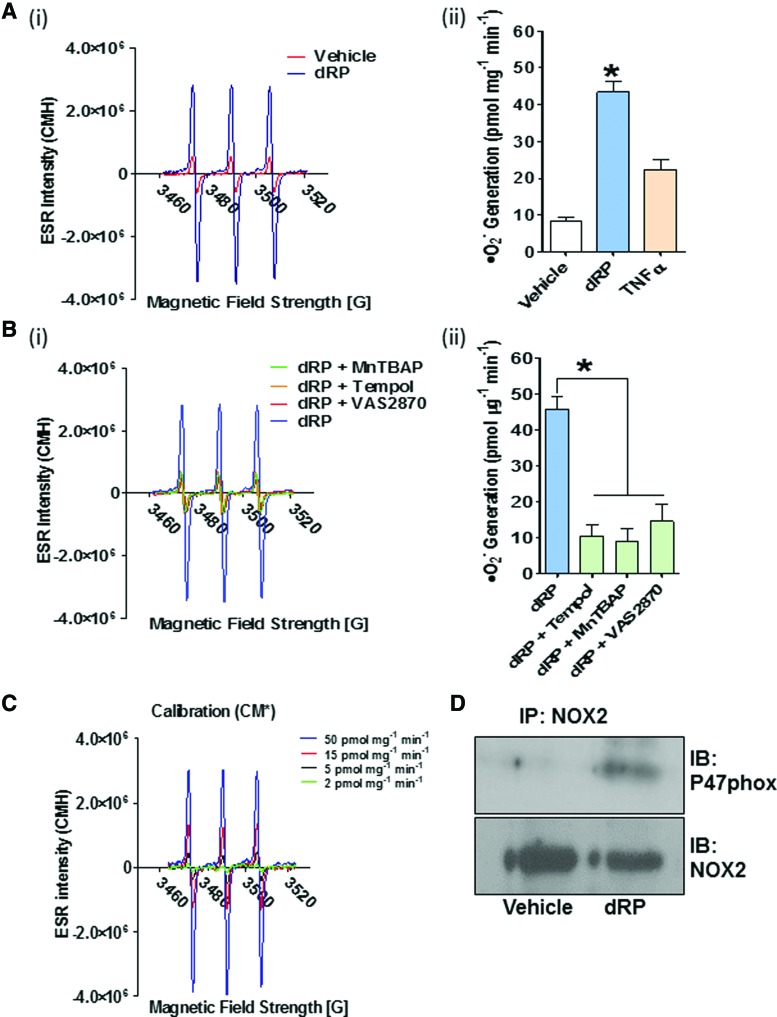
FIG. 2.
dRP stimulates increased levels of ROS generation in HUVECs in an NOX-dependent manner. Quantitative measurements of superoxide anion production in HUVECs were performed using the cell-permeable superoxide-specific spin probe CMH and EPR. (A) Cells were treated for 45 min with 200 μM dRP, vehicle (Tyrode's HEPES buffer), or 50 ng/ml TNF-α in the presence of CMH (200 μM) before EPR analysis. (B) Inhibition of superoxide anion production induced by 200 μM dRP was also detected by EPR by 10 μM MnTBAP, 10 μM Tempol, or 1 μM VAS2870. (A, B) Representative EPR traces are shown (i). The bar charts (ii) show superoxide anion production rates (pmol mg−1 min−1) (mean ± SEM, one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test, *p < 0.05, n = 4). (C) Calibration curve obtained using known concentrations of the oxidized spin probe (i.e., CM*). (D) Activation of NOX2 confirmed by coimmunoprecipitation with p47phox. HUVECs were treated with a vehicle or 200 μM dRP for 1 h. NOX2 immunoprecipitates were subjected to immunoblotting for p47phox and NOX2. Blots are representative of four independent experiments. CMH, 3-methoxycarbonyl-2,2,5,5-tetramethylpyrrolidine; EPR, electron paramagnetic resonance; NOX, NADPH oxidase. To see this illustration in color, the reader is referred to the web version of this article at www.liebertpub.com/ars