Figure 2.
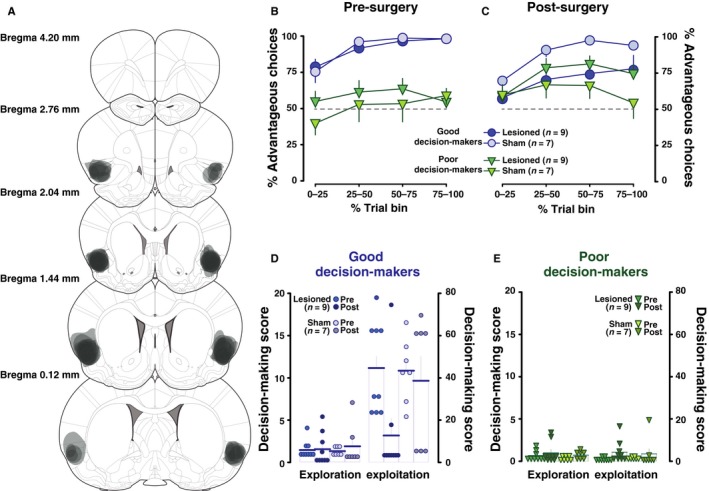
Bilateral AIC lesions impair maximization of reward in rats performing optimally in a rat gambling task. (A) Schematic representation of the extent of the bilateral excitotoxic lesions of the AIC from rats identified as good (n = 16) and poor (n = 16) decision‐makers. Areas shaded in grey represent the extent of neuronal damage. Coronal sections are 4.20 mm anterior through 0.12 mm anterior to the bregma. (B and C) Behavioural performance in the rGT of GDM and PDM rats was not similarly affected by AI lesion. Thus, sham GDM rats, akin to sham PDM, displayed similar performance in rGT prior to, and after surgery. In contrast, GDM lesioned animals showed an impairment in rGT performance as compared to their pre‐lesion test, and PDM lesioned animals exhibited an improvement in their performance, so that the performances of these two groups are similar across the course of the second rGT session. (D) During the exploration phase of the rGT, all good decision‐maker (GDM) rats tended to randomly explore all available options; the decision‐making score defined by the ratio of advantageous choices relative to disadvantageous choices for the same period was around 1 in both lesioned (n = 9) and sham (n = 7) groups before and after surgery. During the last minutes of the test, in this subpopulation the aim of maximizing rewards defined an exploitation phase; it was reflected by a marked preference for advantageous choices. There were around 40 advantageous choices for one disadvantageous choice in lesioned rats before surgery, and in sham rats before and after surgery. But on the other hand, good decision‐makers after AIC lesion showed a ~70% decrease in their decision‐making score. (E) In poor decision‐makers, the exploration phase was also similar through the different groups before and after surgery. Before surgery, in the last minutes of the test, when exploitation of gathered information about options would have been possible, both groups failed to identify the advantageous options as preferable and pursued risky choices; however, lesioned (n = 9) and sham (n = 7) PDM rats increased their exploitation performance by, respectively, 5.5 and 2.5 times during the second rGT despite recombined but matching conditions as compared to the previous one. Data are group means and SEM. Each dot represents an individual. [Colour figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com].
