Figure 3.
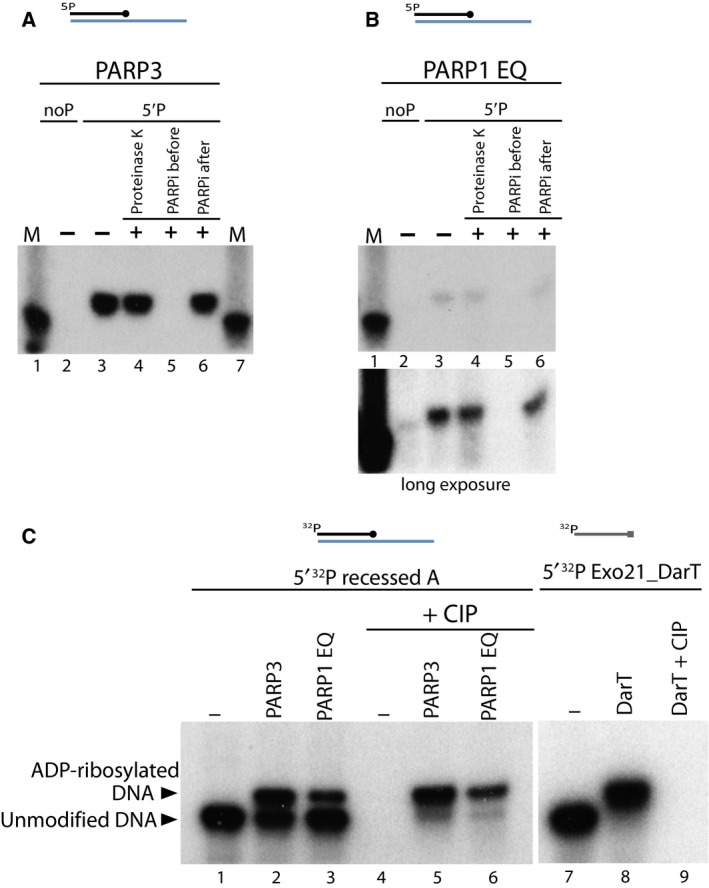
Characterisation of DNA ADP‐ribosylation activity. (A) ADP‐ribosylation of 5′ phosphorylated recessed A substrate catalysed by PARP3 is protected against Proteinase K and SDS treatment. Some reactions were treated with Olaparib, a PARP inhibitor added before the start of reaction or after the ADP‐ribosylation reaction was complete. (B) ADP‐ribosylated 5′P recessed A substrate catalysed by PARP1 E998Q is resistant to Proteinase K and PARP inhibitor treatment. The lower panel indicates a longer exposure of autoradiography. (C) PARP3 and PARP1 E998Q catalysed DNA ADP‐ribosylation is protected against phosphatase activity of CIP. ADP‐ribosylation of 5′ 32P recessed A substrate by PARP3 and PARP1 E998Q protein further treated with or without CIP on left panel. Right panel indicates ADP‐ribosylation of 5′ 32P radiolabelled Exo21_DarT oligo by toxin DarT protein further treated with CIP.
