Fig. 1.
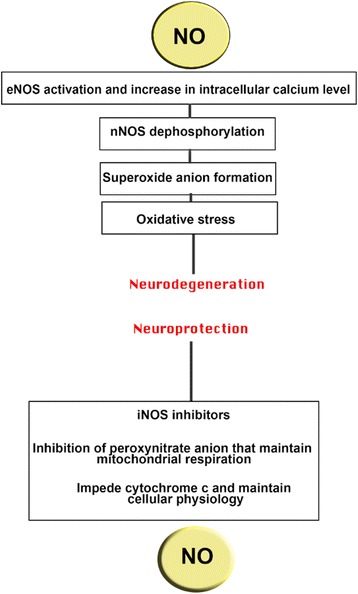
Neuroprotective and neurodegenerative aspects of NO. By activating eNOS (endothelial NO synthase), NO causes neurodegeneration which increases intracellular calcium (Ca2+) level following nNOS (neuronal NO synthase) dephosphorylation and oxidative stress. However, iNOS (inducible NO synthase) inhibitors inhibit peroxynitrite anion which halts cytochrome that maintains homeostasis [55]
