Figure 2.
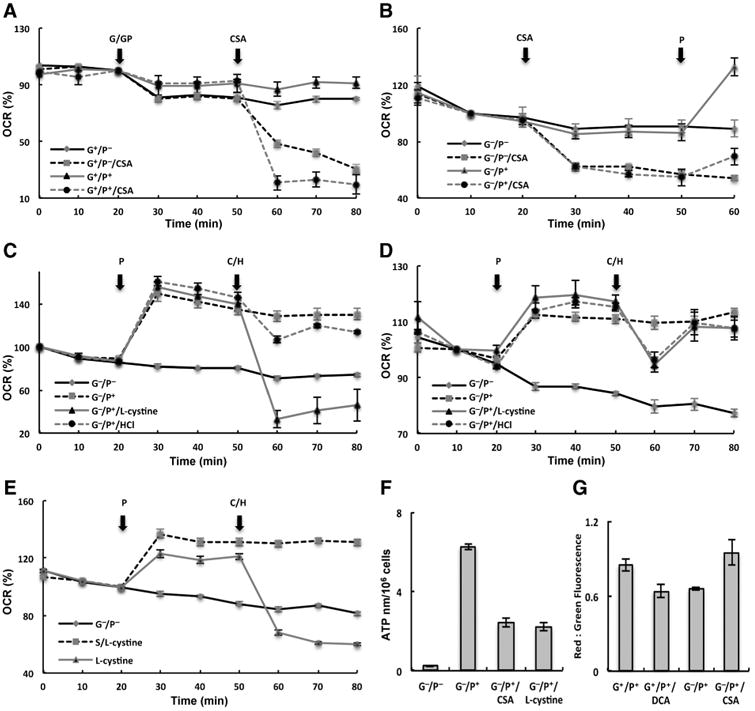
CSA modulates mitochondrial function in glioblastoma cells. A, CSA (1 mmol/L) attenuates OCR in G179 cells in described conditions. G+/P− (P = 0.003); G+/P+ (P < 0.001). B, pretreatment of CSA attenuates pyruvate-induced OCR (P = 0.001). C, l-cystine attenuates OCR in U251 shControl cells (P = 0.008); however, this was abrogated (D) when evaluated in CDO1 stable knockdown cells (shCDO; P = 0.72). E, pretreatment of cells with the system xc− inhibitor sulfasalazine (200 mmol/L) attenuates l-cystine-induced decrease in OCR (P < 0.001). F and G, CSA(1 mmol/L) and l-cystine (100 μmol/L) attenuates ATP synthesis (P < 0.001; F) and increases mitochondrial potential (determined by an increase in red:green ratio in the JC-1 assay; G) in U251 (P = 0.012). Results are representative of at least three independent experiments. G, glucose; P, pyruvate; C, l-cystine; H, HCl; S, sulfasalazine.
