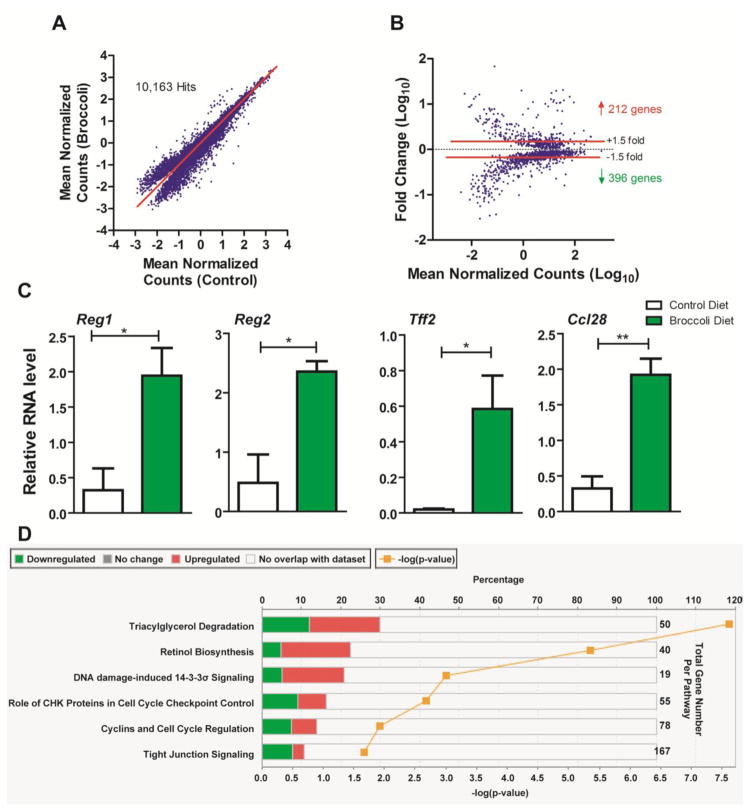
Fig. 7.
RNA-sequencing identified differential colonic gene expression profiles mediated by dietary broccoli in Ahrb/b mice after DSS exposure on day 8. (A) Dot Plot displays distribution of reads that were mapped to known transcripts, deviation from the diagonal indicate differential expression due to broccoli consumption, relative to controls. (B) Bland-Altman plot of Log10 mean normalized (RPKM) counts vs. fold-change in expression. Ingenuity Pathway Analysis identified elevation of 4 genes associated with intestinal health altered by broccoli consumption (Reg1, Reg2, Tff2, and Ccl28). (C) Real time PCR quantification of Reg1, Reg2, Tff2, and Ccl28 normalized to eukaryotic Rpl13a. Data represent the mean gene expression (n=3 per diet group) ± standard error of mean (SEM). (D) Ingenuity Pathway Analysis identified top canonical pathways altered by broccoli consumption in the colon of Ahrb/b mice. For a given pathway, green bars indicate the percentage of down-regulated genes, and red bars indicate the percentage of upregulated genes.