Figure 2. Ecological networks among bacterial species associated with EAC or ESCC risk.
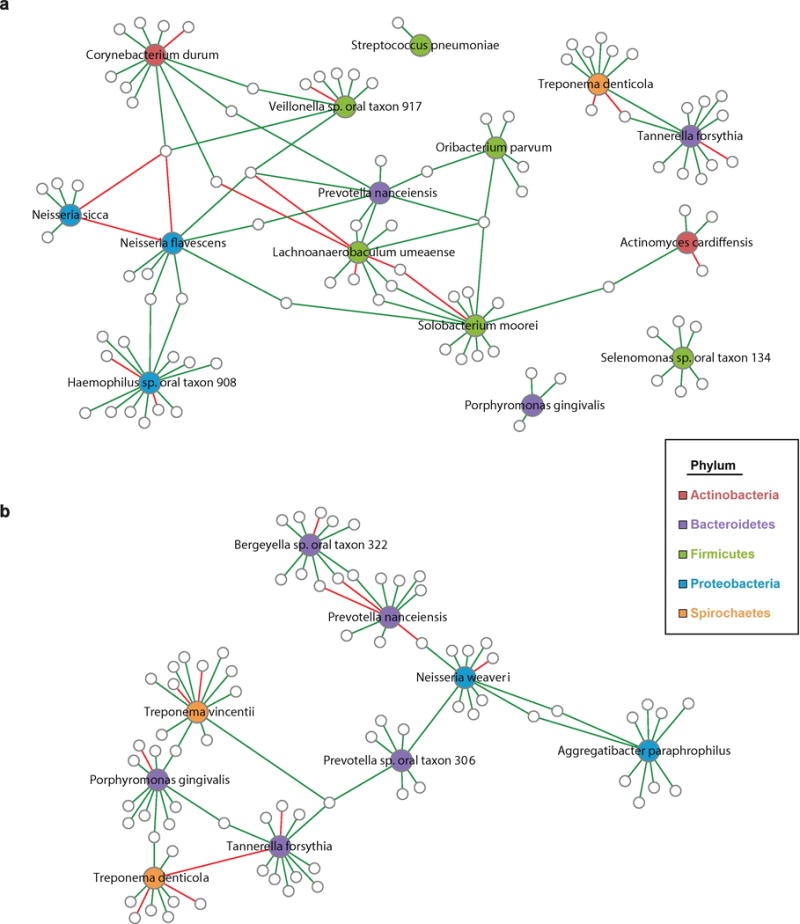
The SPIEC-EASI algorithm (33) was used to infer microbial ecological networks. In (a) algorithm was applied to EAC cases and matched controls (n=241), and only networks related to EAC-associated species or a priori periodontal pathogens are shown. In (b) algorithm was applied to ESCC cases and matched controls (n=75), and only networks related to ESCC-associated species or a priori periodontal pathogens are shown. Species associated with EAC or ESCC are colored by phylum; other species in networks are indicated by small gray-outlined circles. Lines connecting species are colored by sign (positive: green, negative: red).
