Figure 3. Evolved ABEs mediate A•T to G•C base editing at human genomic DNA sites.
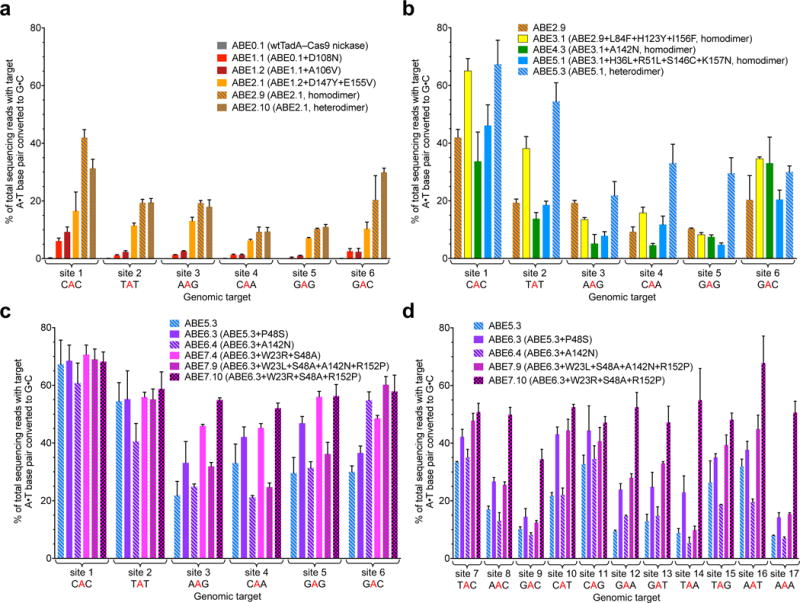
A•T to G•C base editing efficiencies in HEK293T cells of round 1 and round 2 ABEs (a), round 3, round 4, and round 5 ABEs (b), and round 6 and round 7 ABEs (c) at six human genomic DNA sites. d, Editing efficiencies in HEK293T cells of round 6 and round 7 ABEs at an expanded set of human genomic sites. Values and error bars reflect the mean and s.d. of three independent biological replicates performed on different days. Homodimer indicates fused TadA*–TadA*–Cas9 nickase architecture; heterodimer indicates fused wtTadA–TadA*–Cas9 nickase architecture. ABEs in (b) are homodimers except ABE5.3; ABEs in (c) and (d) are all heterodimers.
