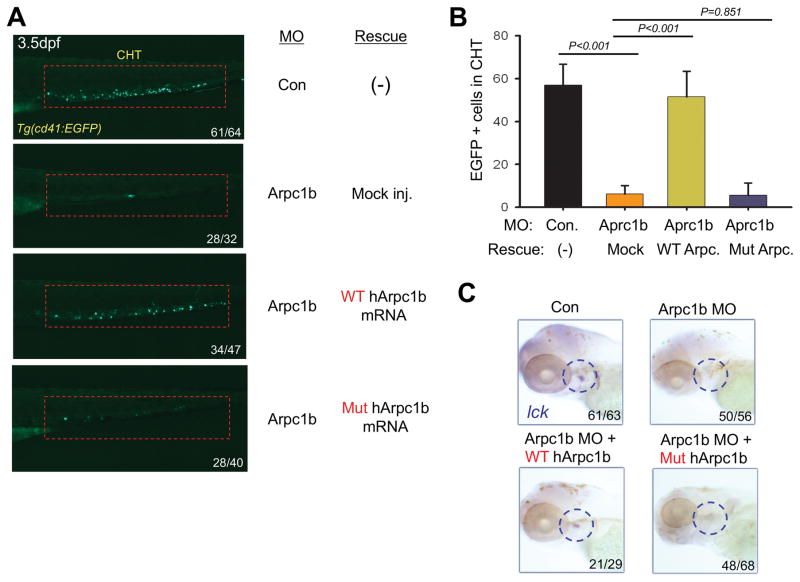
FIGURE 6. Patient mutation in ARPC1B fails to rescue developmental anomalies resulting from Arpc1b knockdown.
A, Overexpression of human WT but not mutant ARPC1B mRNA (150pg) partially rescued the thrombocyte development in 3.5dpf Tg(CD41:EGFP) embryos (lateral view, red rectangles) treated with arpc1b-i3e4 MO (Arpc1b). The numbers refer to the fractions of embryos exhibiting the depicted phenotypes. B, Quantitation of EGFP+ cell numbers in the CHT region as depicted in the red boxes of Fig. 6A as the mean of five embryos of each phenotype. T bar indicates the standard deviation. C, Overexpression ARPC1B in arpc1b morphant embryos using heat-shock inducible plasmids (150pg) encoding WT or mutant human ARPC1B. Developing T cells were identified by performing WISH analysis at 5dpf for using a probe for lck (blue circles, lateral view). The numbers refer to the fractions of embryos exhibiting the depicted phenotypes.