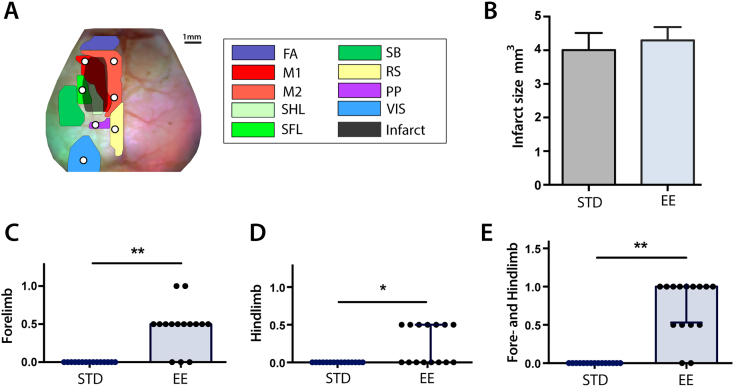
Fig. 1.
Imaging field-of-view, infarct size, and tests of tactile-proprioceptive function.
(A) Dorsal view of the mouse brain; functional assignments within our field-of-view are color-coded according to Paxinos and Franklin (2001). White dots indicate seed location and size. The stroke lesion (black) indicates the 50% lesion incidence of all mice. (B) Infarct size 14 days after stroke (n = 15 mice in each housing condition; p = 0.66). Paw-placement scores of (C) contralesional forelimb, (D) contralesional hindlimb and (E) combined contralesional forelimb and hindlimb 14 days after stroke. Scores are shown as individual data points with group medians and error bars showing upper and lower quartiles (*p < 0.01, **p < 0.001; Mann-Whitney test).
Abbreviations: FA: frontal association, M1: primary motor, M2: secondary motor, SHL: somatosensory hindlimb, SFL: somatosensory forelimb, SB: somatosensory barrel, RS: retrosplenial, PP: posterior parietal, VIS: visual, STD: standard environment, EE: enriched environment.