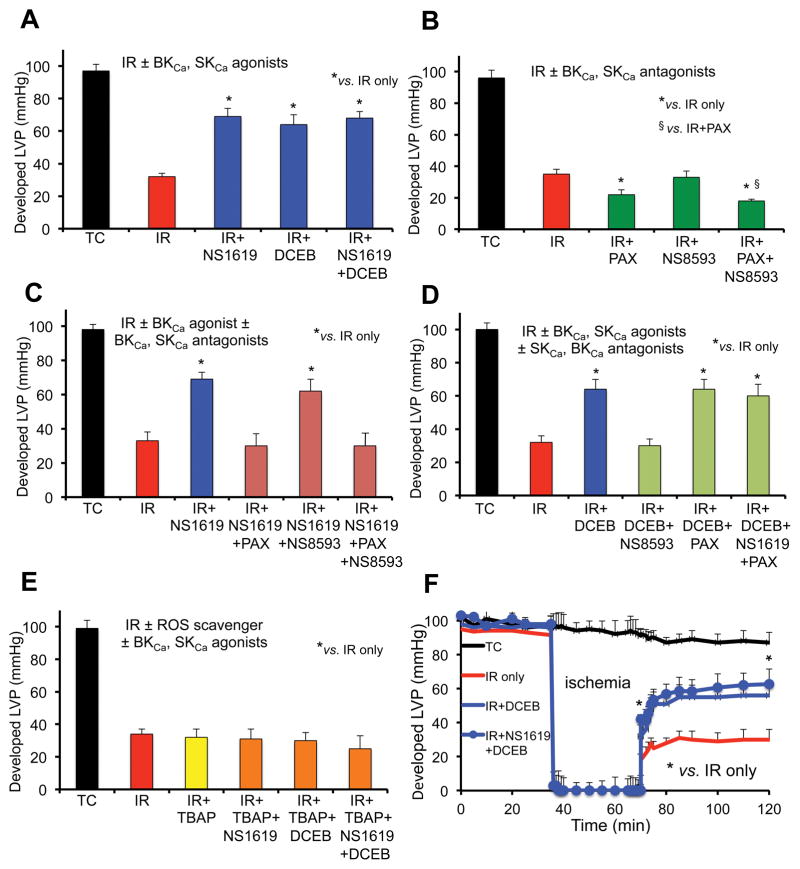
Fig. 1.
Average developed (systolic-diastolic) left ventricular pressure (LVP) 120 min after global IR injury when isolated guinea pig hearts were perfused without ischemia (Time Controls, TC); with 35 min ischemia and 120 min reperfusion (IR); or with IR + BKCa and or SKCa channel agonists (A); IR + BKCa and or SKCa channel antagonists (B); IR + BKCa agonist and or BKCa, SKCa antagonists (C); IR + BKCa agonist and or SKCa or BKCa antagonist (D); and SOD dismutator + BKCa and or SKCa agonist (E). Developed LVP over time for the IR only, IR + SKCa agonist and SKCa + BKCa agonist groups are displayed (F). Note the worsened effects on developed LVP of BKCa and BKCa + SKCa antagonists (green bars) vs. IR only (red bars); the block of protection by the BKCa or SKCa agonists when the BKCa or SKCa antagonists, respectively, was present (green bars); the maintained protection by the BKCa and or SKCa agonists in the presence of either the SKCa or the BKCa antagonist, respectively, (blue bars); and the loss of protection by the SKCa and or BKCa agonists in the presence of SOD inhibition by TBAP (orange/green bars). For each treatment group n = 5–6 hearts; note that for 32 of these hearts’ mitochondria were isolated after 20 min reperfusion to assess RCI and CRC (Figs. 4,5). Data expressed as mean ± sem. *,§ P<0.05.