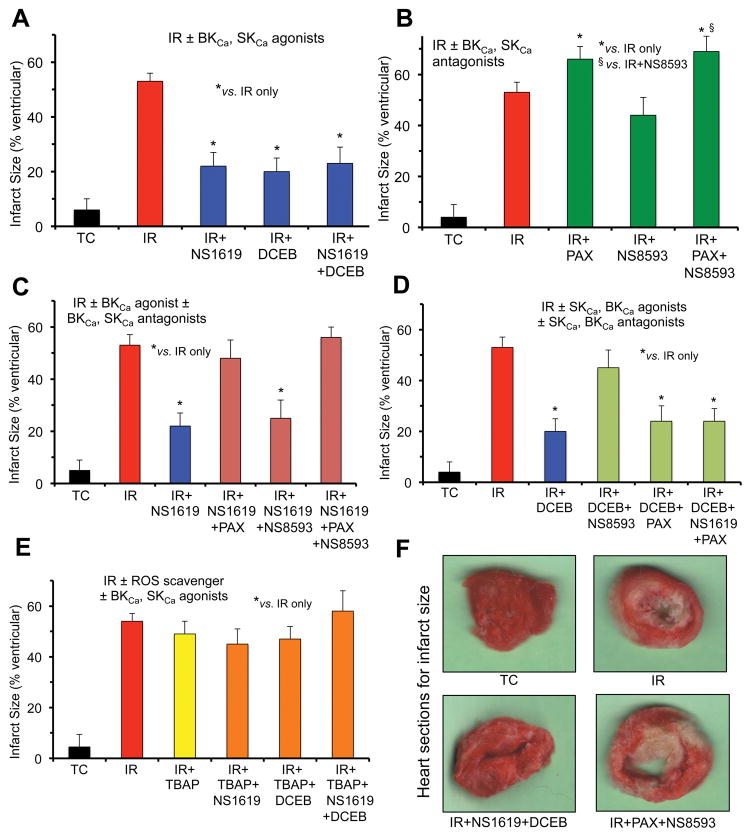
Fig. 2.
Percent infarct size assessed 120 min after global IR injury when the same (Fig. 1) isolated guinea pig hearts were perfused without ischemia (Time Controls, TC); with 35 min ischemia and 120 min reperfusion (IR); or with IR + BKCa and or SKCa channel agonists (A); IR + BKCa and or SKCa channel antagonists (B); IR + BKCa agonist and or BKCa, SKCa antagonists (C); IR + BKCa agonist and or SKCa or BKCa antagonist (D); and SOD dismutator + BKCa and or SKCa agonist (E). Representative hearts from 4 groups displaying normal and infarcted tissue are displayed (F). Note the enhanced infarct size after treatment with BKCa or BKCa + SKCa antagonists (green bars) vs. IR only (red bars); the block of tissue protection by the BKCa or SKCa agonists when the BKCa or SKCa antagonists, respectively, was present (green bars); the maintained reduction in infarct size by the BKCa and or SKCa agonists in the presence of either the SKCa or the BKCa antagonist, respectively, (blue bars); and the loss of protection by the SKCa and or BKCa agonists in the presence of SOD inhibition by TBAP (orange/green bars). For each treatment and control group n=4. *,§P<0.05.