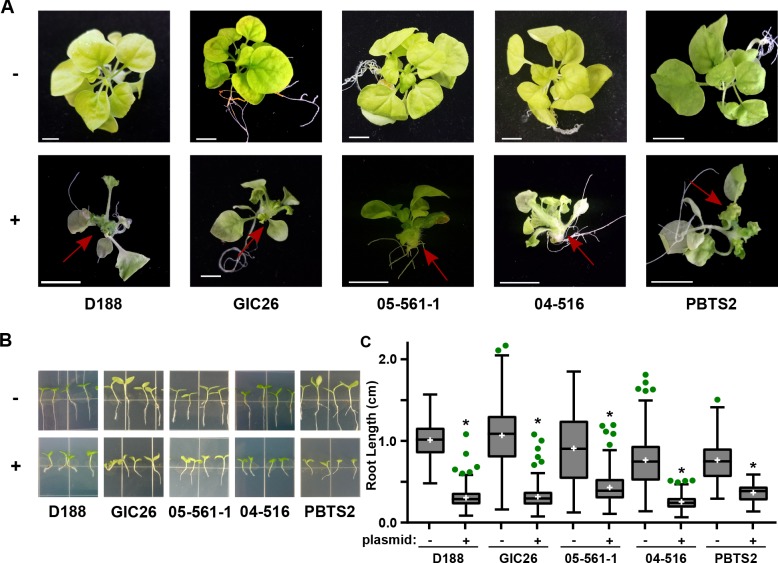
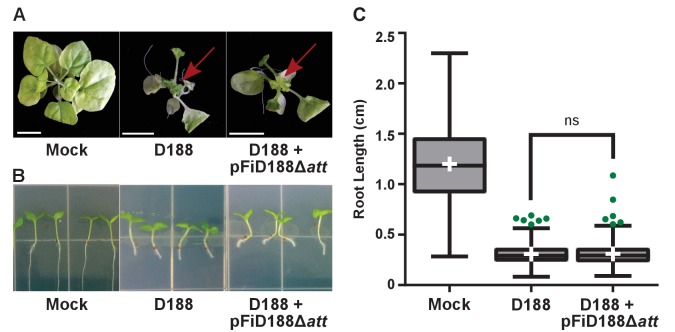
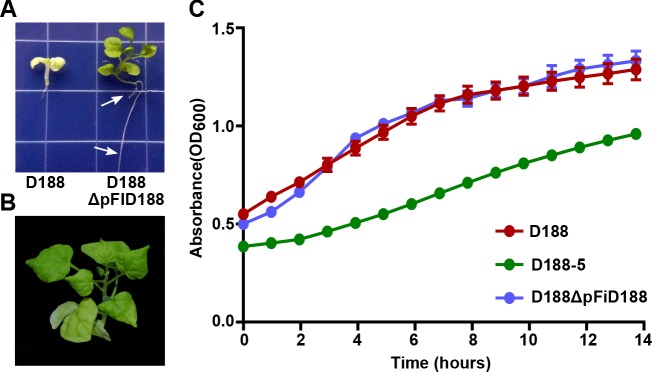
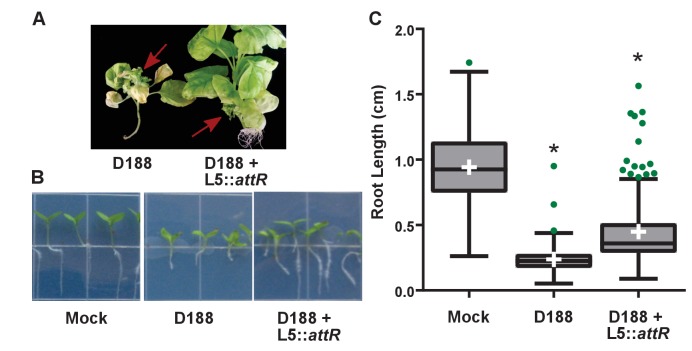
Figure 6. Plasmid pFiD188 with functional fasR and fas is sufficient to transition Rhodococcus isolates to phytopathogens.
(A) Representative images of leafy galls on N. benthamiana. Red arrows indicate leafy galls. Images for GIC26, 04–516, and PBTS2 are repeated from Figure 1. (B) Representative images of the root lengths of seedlings. Three-day-old N. benthamiana seedlings were inoculated with the indicated isolate of Rhodococcus or water (mock) and grown vertically for seven days under constant light. (C) Quantification of the root lengths of N. benthamiana seedlings. In all panels, -/+ indicates absence or presence of pFiD188Δatt. * indicates a significant difference compared to plants treated with the corresponding genotype lacking the plasmid.