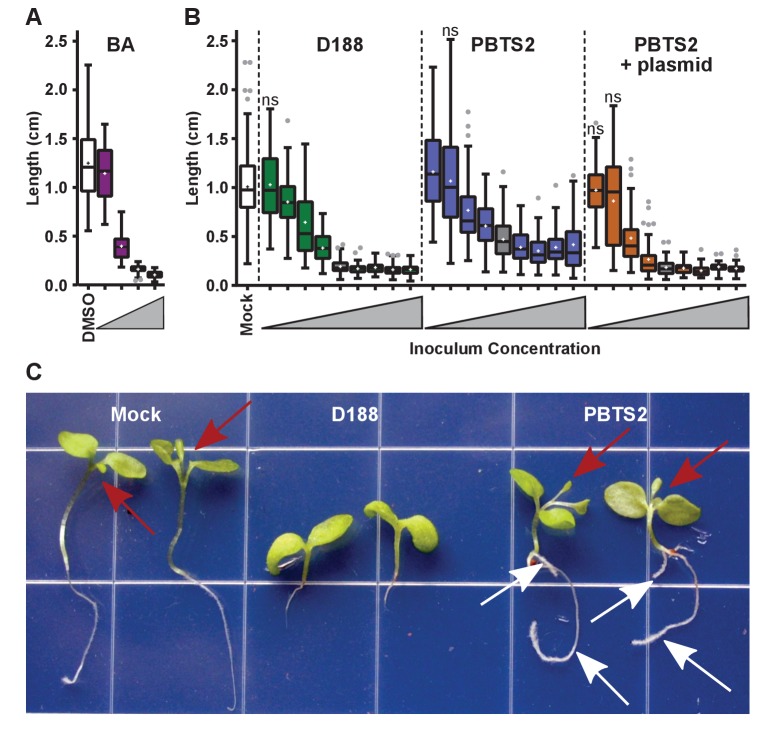
Figure 7. Rhodococcus has a dose-dependent effect on the root elongation of N. benthamiana seedlings.
(A) Quantification of the seedling root lengths of plants grown in exogenously applied cytokinin (6-benyzlaminopurine; BA). Three-day-old N. benthamiana seedlings were transferred to media supplemented with BA (0.01, 0.1, 1.0, and 10 µM) or dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). (B) Quantification of the root lengths of seedlings inoculated with increasing doses of Rhodococcus. Three-day-old N. benthamiana seedlings were inoculated with isolates D188, PBTS2, or PBTS2 + pFiD188Δatt, with doses ranging from 2.5 × 102 to 1.0 × 1012 colony-forming units (cfu). The sample shaded in gray highlights the inoculum of OD600 = 0.5 (1x = 2.5 × 1010 cfu) used in all other assays. Inocula below this decrease in 100-fold intervals. Inocula above increase at 2x, 4x, 10x, and 20x. All treatments are significantly different from mock unless otherwise noted with ‘ns’. (C) Representative image of morphological changes in seedlings. Seedlings inoculated with Rhodococcus D188 or PBTS2 (5 × 1011 cfu; 10x typical amount) or water (mock) were photographed. Red arrows indicate true leaves. White arrows indicate lateral roots and the proliferation of root hairs.