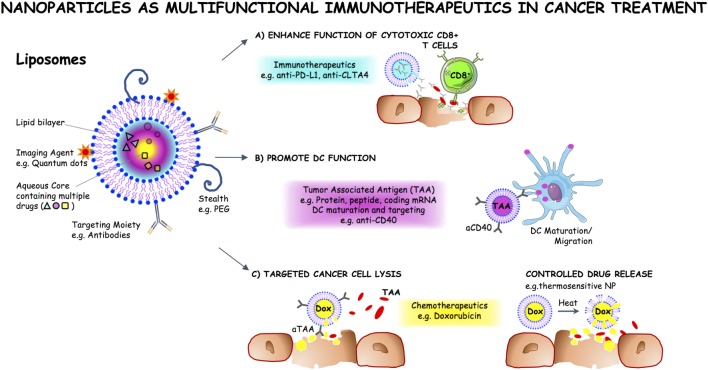
Figure 3.
Multifunctional nanoparticles (NP) in cancer treatment. NP can be tailored to specific applications in tumor immunotherapy using versatile designs of various sizes, constituent biomaterials, and surface modifications. The surface of NP can be functionalized with specific polymers and antibodies to increase their targeting to certain types of cells. Liposomes are self-assembling nanosized vesicles comprised of phospholipids and cholesterol arranged in one or more lipid bilayers enclosing an aqueous core. NP such as liposomes can be used as platforms for the simultaneous delivery of multiple agents, such as (A) immunotherapeutics, e.g., anti-PD-L1 and anti-cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4 (CTLA-4), to enhance the function of tumor-specific effector T cells; (B) tumor-associated antigens (TAA) and adjuvant targeted to dendritic cells (DC) to promote their function; (C) chemotherapeutics and targeted release thereof, for instance, using thermosensitive NP, to promote cancer cell death.