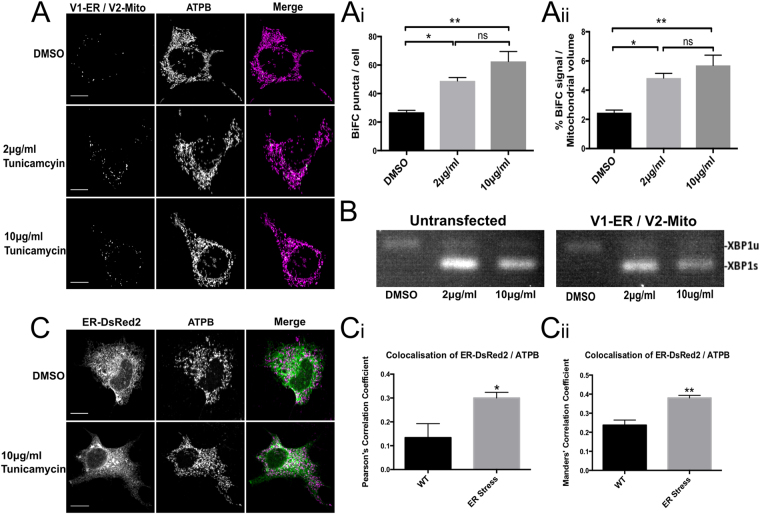
Figure 5.
ER Stress significantly increases the number of ER-mitochondria contacts in NSC34 cells. NSC34 cells expressing V1-ER/V2-Mito were treated with 2 μg/ml or 10 μg/ml tunicamycin to induce an ER stress (A). ER stress significantly increases the mean number of BiFC puncta per cell in and (A(i)) significantly increases the total volume of BiFC signal as a percentage of total mitochondrial volume (A(ii)). n = 3 independent experiments (32–34 cells total). Values indicate mean values of three independent experiments. Error bars indicate SEM. Statistical significance was measured using one-way ANOVA followed by Holm-Sidak’s multiple comparison test, ns (non-significant) P > 0.05, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. ER stress was confirmed by detection of spliced XBP1 mRNA. Expression of the Venus reporter plasmids alone did not induce an ER stress (B). For comparison, in parallel NSC34 cultures the ER and mitochondria were labeled by co-expression of ER-DsRed2 (Green) and anti-ATPB (Magenta) respectively (C). A significant increase in the co-localisation of ER-DsRed and ATPB signals was detected following ER stress induced with 10 μg/ml tunicamycin as quantified by both Pearsons’ Correlation Coefficient (C(i)) and Manders’ Correlation Coefficient (C(ii)). n = 4 independent experiments (26 cells total). Statistical significance was measured using unpaired two-tailed t-test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. Error bars indicate SEM.