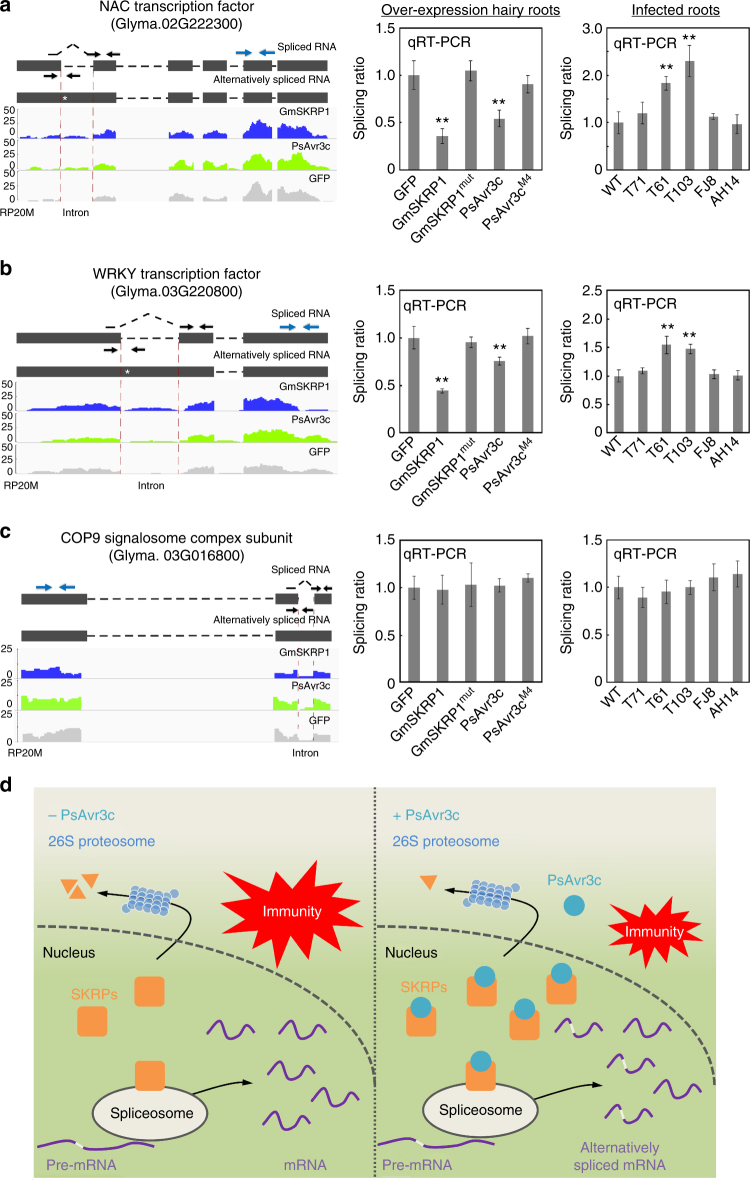
Fig. 8.
Validation of defense-related genes pre-mRNAs splicing ratio by qRT-PCR. a–c Selected gene splicing ratio and gene expression was determined by RNA-seq and qRT-PCR analyses. The GmNAC and a GmWRKY predicted transcription factor genes are subject to AS in the GmSKRP1 and PsAvr3c overexpressing lines, whereas the COP9 signalosome complex subunit gene does not. The left panel shows wiggle plots of RNA-seq data with the schematic gene model, the asterisks indicate the premature stop codon. The black and blue arrows indicate the primers that are used to measure the intron splicing ratio and gene relative expression, respectively. The spliced primers that cross exon-exon junctions are shown with dashed lines over the intron. Splicing ratio was calculated by determining the level of spliced RNA normalized to the level of unspliced RNA. Values on the Y-axis indicate reads per 20 million (RP20M). The right panel shows the selected genes splicing ratio of introns in five different overexpression hairy roots and six different infection roots. Pre-mRNA intron splicing ratio from three replicates are normalized and presented as means ± standard errors (**P < 0.01; one-way ANOVA). d Schematic representation of PsAvr3c virulence function. In absence of PsAvr3c effector (left), GmSKRPs are consistently degraded by 26S proteasome probably for maintaining protein turnover. SKRPs associate with spliceosome components to regulate pre-mRNA splicing. Proper splicing of defense-related genes contribute to plant resistance. In the presence of PsAvr3c effector and the absence of Rps3c (right), PsAvr3c associates and stabilizes SKRPs in plant nucleus. Increased level of SKRPs results in large scale of pre-mRNA alternative splicing. In particular, some defense-related genes generate alternative splicing isoforms, thus the PsAvr3c effector reprograms host pre-mRNA splicing to suppress plant immunity