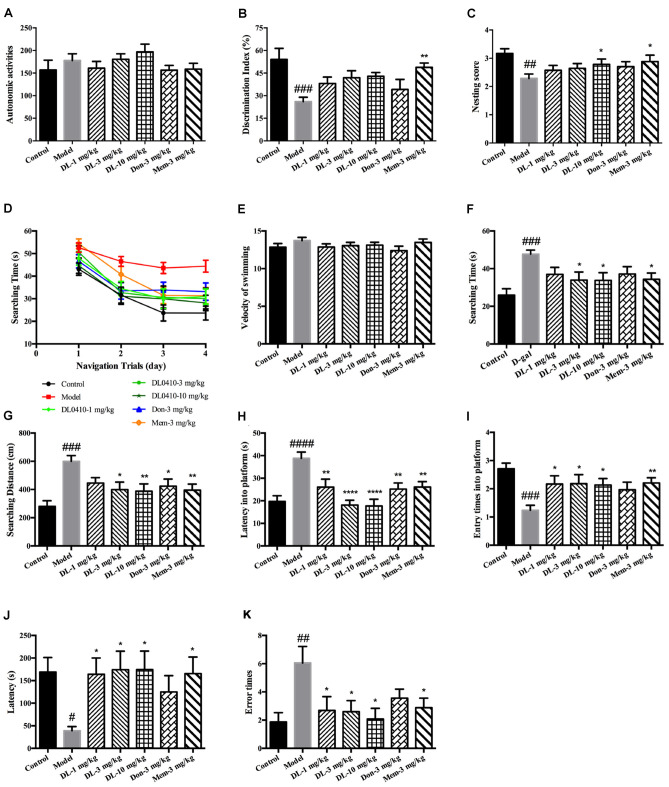
Figure 2.
DL0410 could improve memory and cognition of D-galactose-administered mice in behavioral tests. Data are the mean ± SEM (n = 16–20). (A) There were no differences among groups in the autonomic activities of mice administered D-galactose and DL0410. (B) DL0410 tended to increase the discrimination index (DI) of mice in the novel-object recognition test (F(6,83) = 3.946, p = 0.0016). (C) DL0410 could increase the nesting score of mice in the nest-building test (F(6,111) = 2.532, p = 0.0246). (D–I) The effect of DL0410 on the spatial memory of mice in the Morris water maze. (D) The searching time of mice decreased as the training time went on in the navigation trials (time effect F(3,446) = 39.80, p < 0.0001; treatment effect F(6,446) = 10.22, p < 0.0001). (E) DL0410 had no effect on the velocity of swimming of mice. (F) DL0410 could shortened the searching time of mice on the fourth day of navigation trials (F(6,113) = 3.326, p = 0.0047). (G) DL0410 could decrease the searching distance of mice on the fourth day of navigation trials (F(6,113) = 4.789, p = 0.0002). (H) DL0410 could decrease the latency of mice crossing the platform in the probe trial (F(6,113) = 3.895, p = 0.0016). (I) DL0410 could increase the entry times of mice crossing the platform in the probe trial (F(6,111) = 7.587, p < 0.0001). (J–K) The effect of DL0410 on the performance of mice in the step-through test. (J) DL0410 could prolong the latency of mice stepping into the black chamber (F(6,107) = 2.747, p = 0.0171). (K) DL0410 could reduce the error times of mice stepping into the black chamber (F(6,107) = 2.990, p = 0.0097). #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001, ####p < 0.0001 vs. control group, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ****p < 0.0001 vs. model group.