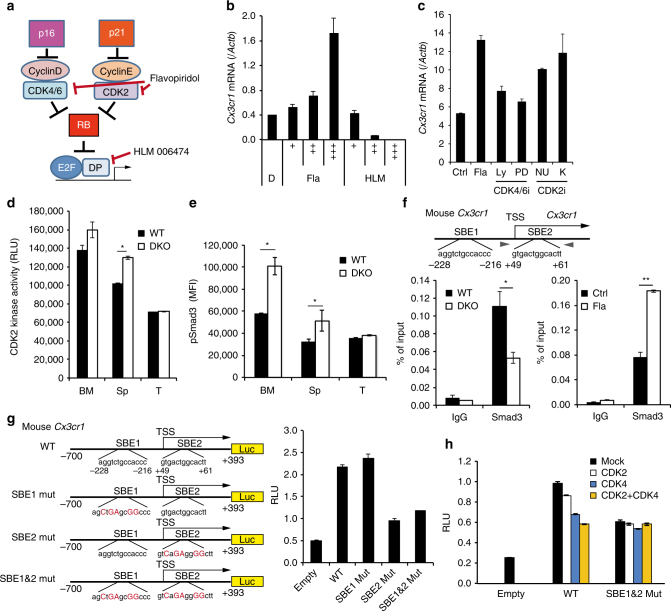
Fig. 5.
CDK-mediated SMAD3 phosphorylation inhibits Cx3cr1 expression. a Diagram of the CDKI-CDK-RB-E2F pathway and sites of action of chemical inhibitors. b Expression of Cx3cr1 mRNA in BM-Mo-MDSCs treated with indicated doses of flavopiridol (Fla), HLM006474 (HLM) or dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) control (D). b “+” indicates drug concentration: Fla; + (4 nM), ++ (20 nM), +++ (100 nM). HLM; + (2 nM), ++ (10 nM), +++ (50 nM). c Expression of Cx3cr1 mRNA in BM-Mo-MDSCs treated with flavopiridol (Fla; 50 nM), LY2835219 (Ly; 5 nM), PD 0332991 (PD; 5 nM), NU6027 (NU; 5 μM), K03861 (K; 250 nM) or DMSO (Ctrl). d Kinase activity of CDK2 against recombinant SMAD3. CDK2 was immunoprecipitated from lysates of Mo-MDSCs purified from bone marrow (BM), spleen (Sp) and tumour (T). e Flow cytometric analysis of phosphorylated Smad3 (S213). Graphs indicate mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of indicated protein expression in Mo-MDSCs (n = 4). f Smad3 binding to the Cx3cr1 promoter region was evaluated by ChIP. Lysates were prepared from BM-Mo-MDSCs derived from WT or p16/p21-DKO mice (left). WT BM-Mo-MDSCs were treated with 100 nM flavopiridol (Fla) for 24 h (right). Two SBEs are located around the transcriptional start site (TSS) of the mouse Cx3cr1 gene. Arrowheads indicate primer positions. g, h Schematic representation of mouse Cx3cr1 promoter reporter constructs; two SBEs (SBE1 and SBE2) are shown in the sequence, and mutation sites are indicated by red uppercase letters. THP-1 cells were transfected with the indicated reporter plasmids and pCMV-Renilla (g). Where indicated, cells were also co-transfected with expression plasmids encoding CDK2, CDK4 or both (h). At 48 h after transfection, the luciferase activities were measured. Data are representative of three biological replicates and presented as the mean ± SEM. The statistical significance was determined by Student’s t-test; *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01