FIGURE 1.
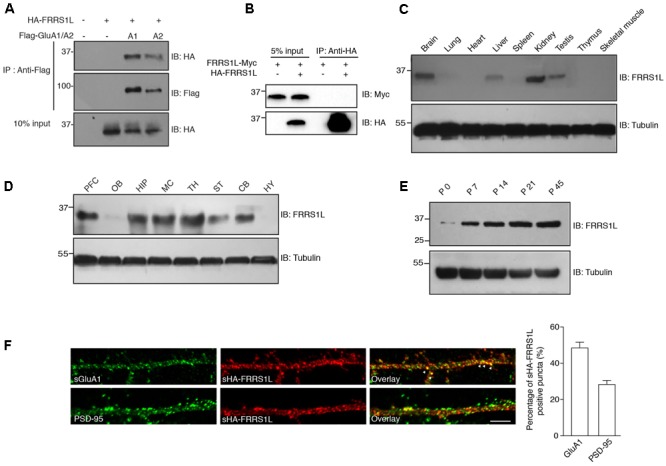
Basic characterization of FRRS1L protein in mice. (A) Co-IP of FRRS1L with GluA1 or GluA2(Q) in HEK cells. Lysates from HEK cells transfected with HA-FRRS1L alone, HA-FRRS1L together with Flag- GluA1 or GluA2(Q), or an empty vector as a control, were immunoprecipitated with an anti-Flag antibody. The IPs and 10% input were probed with indicated antibodies. IB, immunoblotting. N = 3 independent repeats. (B) FRRS1L did not form dimers or oligomers in HEK cells. Lysates from HEK cells transfected with FRRS1L-Myc alone or together with HA-FRRS1L were immunoprecipitated with an anti-HA antibody. The IPs and 5% input were probed with indicated antibodies. N = 3 independent repeats. (C) Tissue distribution of endogenous FRRS1L in adult mouse. N = 4, n = 5 animals. (D) Expression profile of FRRS1L in adult mouse brain tissues. PFC, prefrontal cortex; OB, olfactory bulb; HIP, hippocampus; MC, motor cortex; TH, thalamus; ST, striatum; CB, cerebellum; HY, hypothalamus. N = 3 independent repeats from 6 animals. (E) Developmental profile of FRRS1L expression in mouse hippocampus. N = 4 independent repeats. (F) Representative images show that surface HA-FRRS1L (sHA-FRRS1L) in mouse dissociated hippocampal neuron cultures at DIV16 partially co-localizes with surface GluA1 (sGluA1), but the majority of sHA-FRRS1L does not co-localize with an excitatory synapse marker, PSD-95. Arrowheads indicate the co-localization of sHA-FRRS1L with sGluA1. The bar graph in right shows the percentage of co-localization. Scale bar, 20 μm. N = 3 independent repeats. Uncropped scans of Western blots in Supplementary Figures 1A–E.
