Fig. 6.
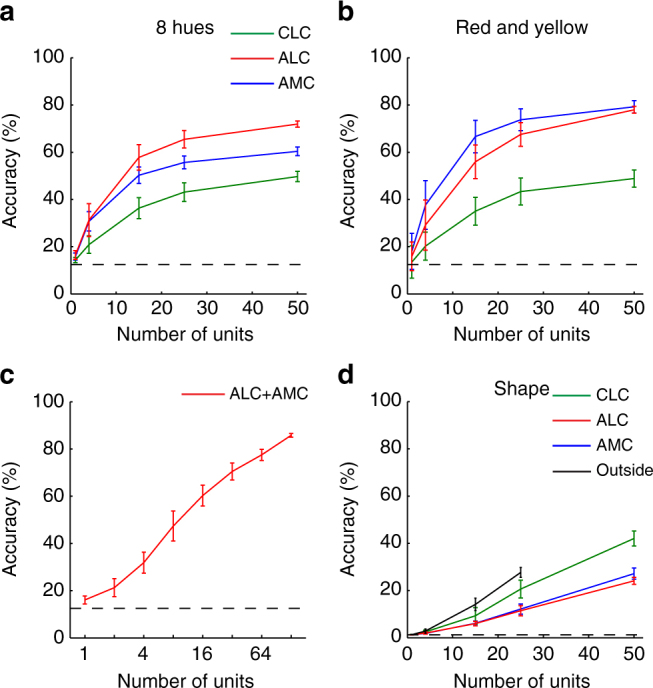
Decoding shape-invariant color and color-invariant shape from color patches. a SVM models were trained to classify hues independent of shape. The population response of a set of randomly-selected units was used as the input to each model. Half of the trials were used for training and the remaining half for cross-validation. Shape-invariant hue could be significantly better decoded by AMC and ALC populations than by CLC (for 50 units, p < 0.01 for both comparisons, 2000 iterations of bootstrapping). Furthermore, ALC showed better overall decoding than AMC (p = 0.013). Dashed line indicates chance level (1/8 = 12.5%). Results are averages across 2000 iterations of random sampling. Errorbars represent s.d. b similar to (a), but only quantifies decoding accuracy for two hue categories: red and yellow. Decoding based on AMC is better than ALC, but not significant (p = 0.185). c similar to (a), but for a combined population of anterior color-patch neurons. d similar to (a), but for hue-invariant shape decoding. CLC is significantly better than ALC and AMC (for 50 units, p < 0.01 between CLC and ALC, p = 0.028 between CLC and AMC). Furthermore, neurons outside color patches showed better performance than color-patch neurons, but only significantly better than ALC and AMC (For 25 units, p < 0.01 between outside and ALC, p = 0.019 between outside and AMC and p = 0.186 between outside and CLC). Dashed line indicates chance level (1/82 = 1.2%)
