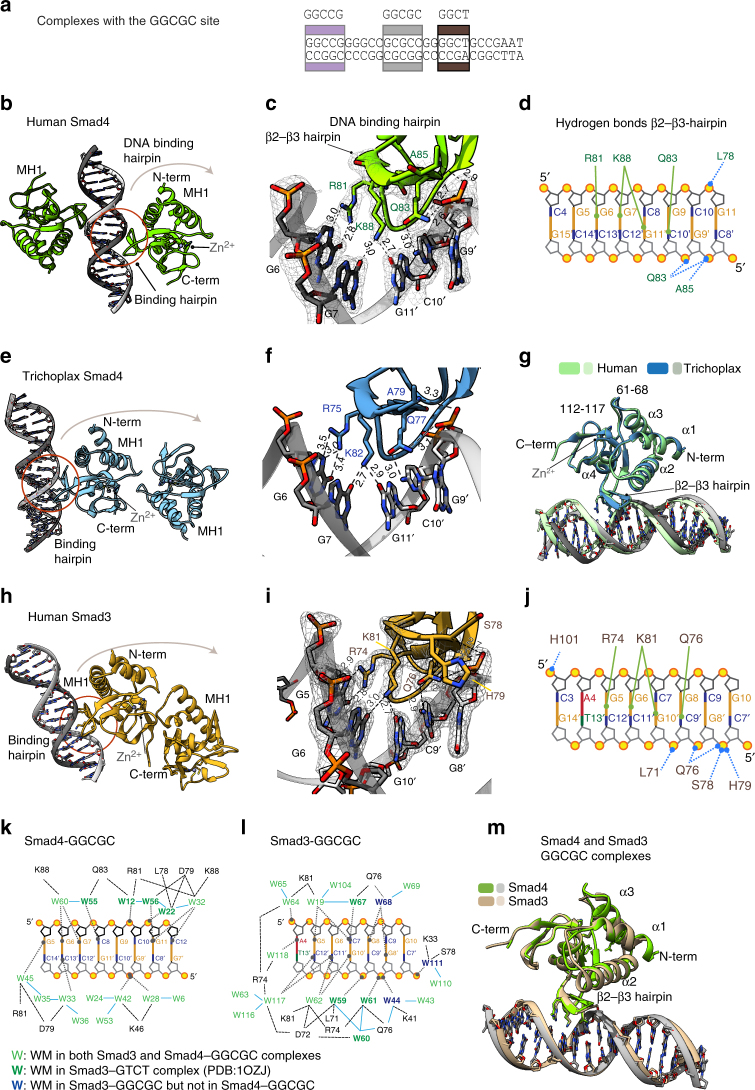
Fig. 4.
Smad4 and Smad3 MH1 domains bound to the GGCGC site. a Schematic representation of the GC1 site with the crystallized regions highlighted in gray. DNA sequences are shown in Supplementary Table 1. b Biological assembly of huSmad4 MH1–GGCGC complex (2.05 Å resolution). The hairpin binding site is circled. The bound Zn2+ and coordinating residues are shown. c A close view of the GGCGC recognition. Distances are shown in Å. The electron density corresponding to the binding region is contoured at 1σ level (2Fo-Fc). The stereoview representation of the complexes is shown as Supplementary Fig. 9. d Intermolecular contacts. Solid lines indicate hydrogen bonds between protein residues and DNA bases. Dashed lines indicate hydrogen bonds between residues and DNA phosphates. Bases are colored and labeled. e ASU of Trichoplax adhaerens Smad4 MH1 (shown in blue) with the GGCGC site (2.43 Å). f Specific intermolecular contacts of taSmad4 MH1 with the GGCGC site. Distances shown in Å. g Superposition of the Human (green) and Trichoplax (blue and gray) Smad4 MH1 complexes with the same GGCGC DNA. Protein loops displaying minor structural differences are indicated (numbers correspond to the human sequence). h ASU of the huSmad3 MH1 in complex with the same GGCGC (2.05 Å). i Expanded view of the GGCGC site with bound Smad3. The electron density corresponding to the binding region is contoured at 1σ level (2Fo-Fc). j Intermolecular contacts for the huSmad3 MH1 in complex with the GGCGC site. k Summary of specific DNA–protein interactions mediated by water molecules for the huSmad4–GGCGC complex. Hydrogen bonds are represented by black dashed lines. Water molecules common to the huSmad3 GTCT complex (PDB:1OZJ) are shown in bold green, water molecules present in both Smad4 and Smad3 complexes are shown in green. Analyzed waters were selected as described in the Methods section (numbers correspond to those in the PDB files). l Summary of specific DNA–protein interactions mediated by water molecules for the Smad4–GGCGC complex, as in k. Waters only present in the Smad3 complex are shown in blue. m Superposition of the huSmad3 (tan) and huSmad4 (chartreuse) GGCGC complexes. Minor differences are detected at the α1–α2 and after α3. The DNA-binding site is nearly identical