Figure 3.
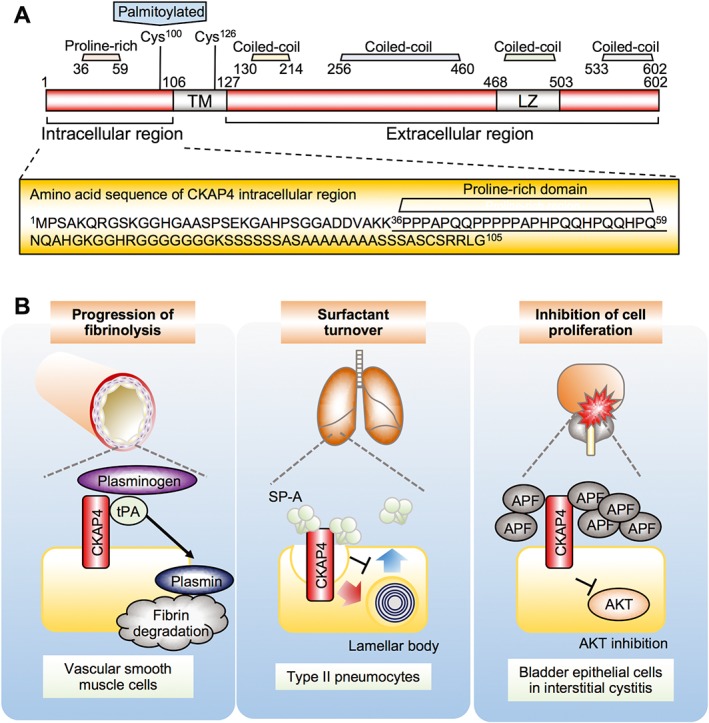
Structure and functions of CKAP4 in the cell surface membrane. (A) Schematic diagram of CKAP4. Amino acid residues in the CKAP4 intracellular region are enlarged, showing no tyrosine residues. The proline‐rich motif that interacts with the p85 subunit of PI3K is underlined. Cys, cysteine; TM, transmembrane. (B) Possible functions of CKAP4 in the cell surface membrane. Left panel, tPA binds to CKAP4 and regulates plasmin production and progression of fibrinolysis in vascular smooth muscle cells. Middle panel, SP‐A binds to CKAP4 and induces CKAP4 internalization and regulates secretion of lamellar body. Right panel, APF binds to CKAP4 and inhibits cell proliferation through the suppression of Akt in bladder epithelial cells.
