Figure 6.
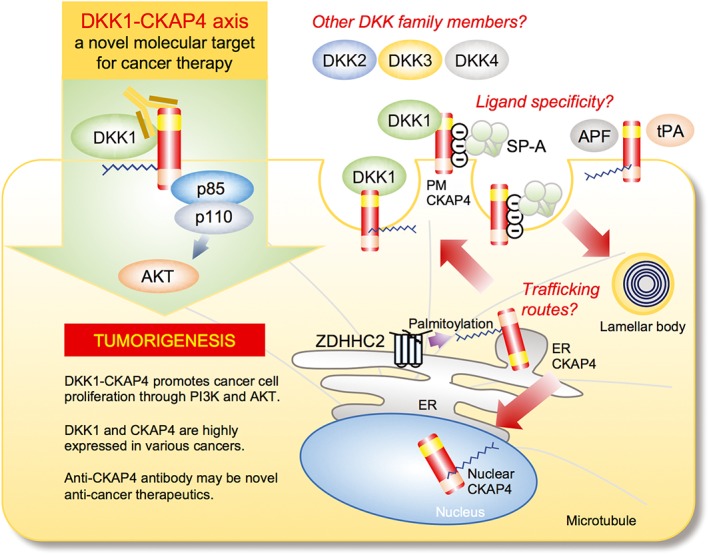
The DKK1–CKAP4 axis as a novel molecular target for cancer therapy and future perspectives. Upon binding to CKAP4, DKK1 promotes cancer cell proliferation through the activation of PI3K and Akt. Anti‐CKAP4 antibody inhibits the binding of DKK1 to CKAP4 and xenograft tumour formation. There are questions to be addressed. (1) ‘Trafficking routes’: it is unclear how subcellular localization of CKAP4 is regulated. Although CKAP4 functions as a receptor, CKAP4 is mainly localized to the ER. Post‐translational modification, such as palmitoylation at Cys100 by DHHC2, could be involved in the subcellular localization of CKAP4. (2) ‘Other Dkk family members’: it is unknown whether other DKK family members also act as a ligand for CKAP4. Since CRD‐1 is conserved among the four DKK genes, DKK2, 3 and 4 would interact with CKAP4. (3) ‘Ligand specificity’: Although several ligands for CKAP4 other than DKK1 have been identified, the specificity of the binding between CKAP4 and ligands has not been addressed. See details in the text.
