Figure 1.
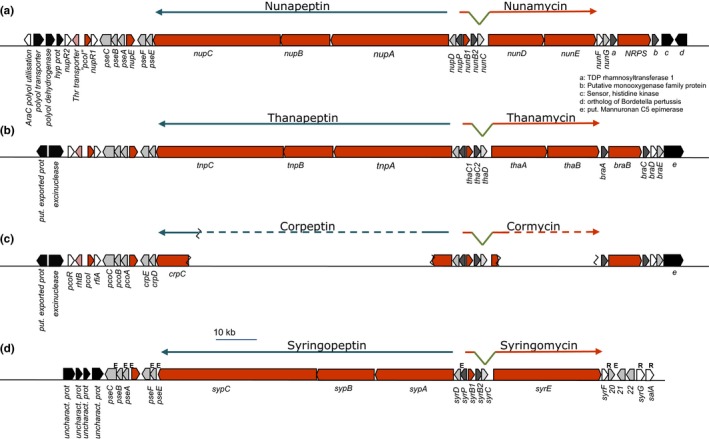
Organization of the nun and nup gene clusters in Pseudomonas fluorescens In5 and comparison with other pseudomonads. Map of the nunamycin (nun) and nunapeptin (nup) gene clusters located on a genomic island spanning over 100 kb in strain In5. Gene clusters harbor nunF and all the known biosynthetic genes for nunamycin and nunapeptin, including the left and right border regions (a) and comparison with the thanapeptin and thanamycin gene clusters from Pseudomonas sp. SHC52 (b) and the corpeptin and cormycin gene clusters from P. corrugata CFBP5454 (c) and the syringopeptin and syringomycin gene clusters from P. syringae pv. syringae B738a (d). The solid orange arrows indicate the biosynthesis genes, and regulatory genes are depicted by white arrows, whereas genes with secretory functions are represented by gray arrows with additional genes shown in dark gray arrows
