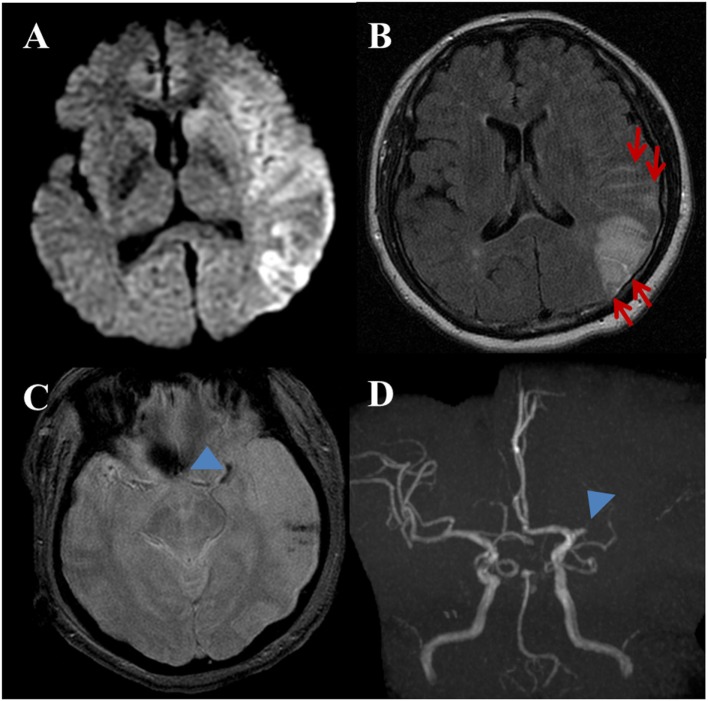
Figure 2.
A 53-year-old female with a complaint of acute onset aphasia. Stroke due to cardioembolic. (A) DWI shows large diffusion restricted lesion on the left frontoparietotemporal lobes. (B) Post-contrast fluid-attenuated inversion recovery image shows sulcal enhancement along the left frontoparietal sulci (arrows) compatible with hyperintense acute reperfusion marker. (C) Gradient-echo imaging image shows blooming artifact at the left proximal MCA (arrowhead) indicating intravascular thrombus. Note, hemorrhagic foci of stroke area at the left temporal lobe. (D) Three-dimensional time-of-flight MRA shows occlusion of proximal M1 segment of left MCA (arrowhead). There is no stenoocclusive lesion in the cervical arteries (not shown).