Fig. 2.
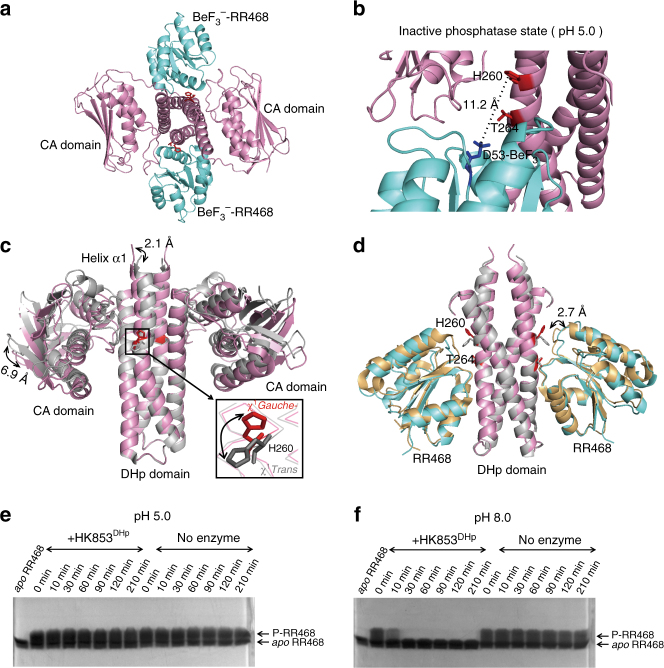
Crystal structure of the HK853cp-BeF3 −-RR468 complex at low pH reveals a catalytically inactive state. a The structure of the HK853cp-BeF3 −-RR468 complex at pH 5.0. The BeF3 −-RR468 substrate is shown in cyan, the HK853cp dimer in pink, and the sidechains of H260 and T264 of HK853cp in red. b Structural details of the inactive state of the HK853cp-BeF3 −-RR468 complex at pH 5.0. The BeF3 −-D53 residue of RR468 is shown in blue, and the distance between the ε-N atom of H260 and the Be atom is labeled. c A pH-gated conformational switch of HK853cp. Superimposed structures of the inactive state (pink, with the sidechain of H260 in red; this structure) and active state (gray, PDB 3DGE) of the HK853cp-BeF3 −-RR468 complex demonstrate the sidechain flipping of H260 and the movements of the CA domain and the N-terminal α1-helix of the DHp domain. The distances between Cα atoms of C359 of the CA domain and between Cα atoms of R246 of the DHp domain in the two structures are labeled. For visual clarity, RR468 is not displayed. The χ 1 rotameric states of H260 in the two structures are labeled. d Structural movement of RR468 in the HK853cp-BeF3 −-RR468 complex between the inactive state (with RR468 shown in cyan) and active state (with RR468 shown in orange). The distance between Cα atoms of G87 in the two structures is labeled. For visual clarity, the CA domains are not displayed. Structural overlays in c, d are generated by superimposing the α2-helix and the C-terminal half of the α1-helix (residues of 266–317) of the DHp domain of HK853cp. e, f show the differential phosphatase activities of HK853DHp detected by the Phos-tag gel shift assay at pH 5.0 and pH 8.0, respectively