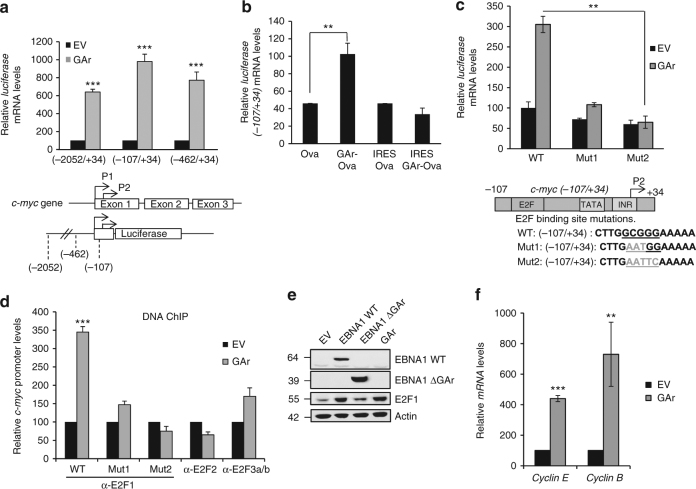
Fig. 2.
E2F1 promotes GAr-dependent induction of c-myc. a RT-qPCR data show the relative induction of c-myc-luciferase (Renilla) reporter constructs (indicated in lower panel) following expression of the GAr, as compared to control plasmid (EV). b Relative RT-qPCR values show the induction of c-myc promoter activity from the (−107/+34) luciferase reporter construct using indicated Ova and GAr-Ova (±IRES) cDNA constructs. c Relative RT-qPCR values from the (−107/+34) luciferase reporter constructs carrying either three (Mut1) or five (Mut2) point mutations in the E2F1 consensus binding site (indicated in lower panel). d DNA chromatin IP (ChIP) assay using the (−107/+34) sequence of the c-myc promoter constructs (WT, Mut1 and Mut2) and antibodies against E2F1, E2F2 or E2F3 from cells expressing the GAr or EV. e Western blots showing the E2F1 levels in cells expressing EV, EBNA1 WT, EBNA1 ∆GAr or GAr with actin used as loading control. f RT-qPCR data of the induction of the E2F1 target genes Cyclins E and B following expression of GAr. For RT-qPCR, the values were normalised with GAPDH. The values represent the mean data from three independent experiments with s.d. Significance was calculated using t tests (***p < 0.001 and **p < 0.05)