Figure 3.
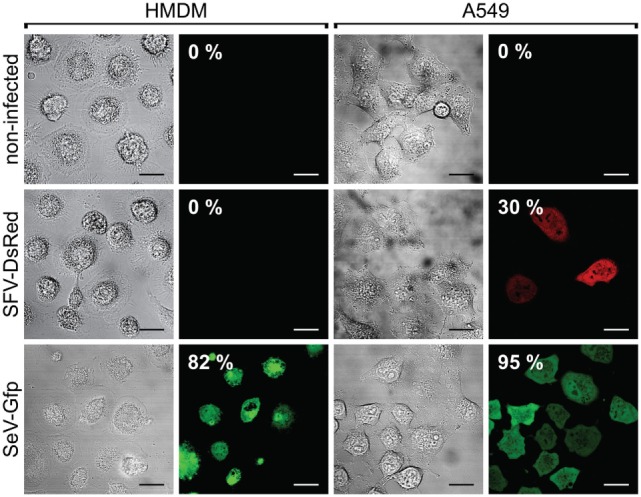
Human macrophages are resistant to Semliki Forest virus (SFV) infection. Human monocyte-derived macrophages (HMDMs), and the human lung carcinoma cell line A549 were infected with either SFV-DsRed or SeV-Gfp virus particles. The resulting cell monolayers were analyzed using phase-contrast microscopy, and the expression of DsRed and GFP was evaluated using fluorescence microscopy 24 h post-infection (scale bars, 20 µm). The numbers in the images indicate the percentages of infected cells. Non-infected cells were used as negative controls. HMDMs were not susceptible to infection with SFV-DsRed, whereas A549 cells were infected with SFV, as expected (shown in the second row). Sendai virus (SeV)-Gfp virus particles were used as a positive control because they are capable of infecting both HMDMs and A549 cells, as shown in the third row. Total HMDM resistance to SFV infection was confirmed in three independent experiments using HMDMs from different donors. Data from one representative experiment are shown where the percentages represent average fluorescent protein-expressing cell population with SEM <5%.
