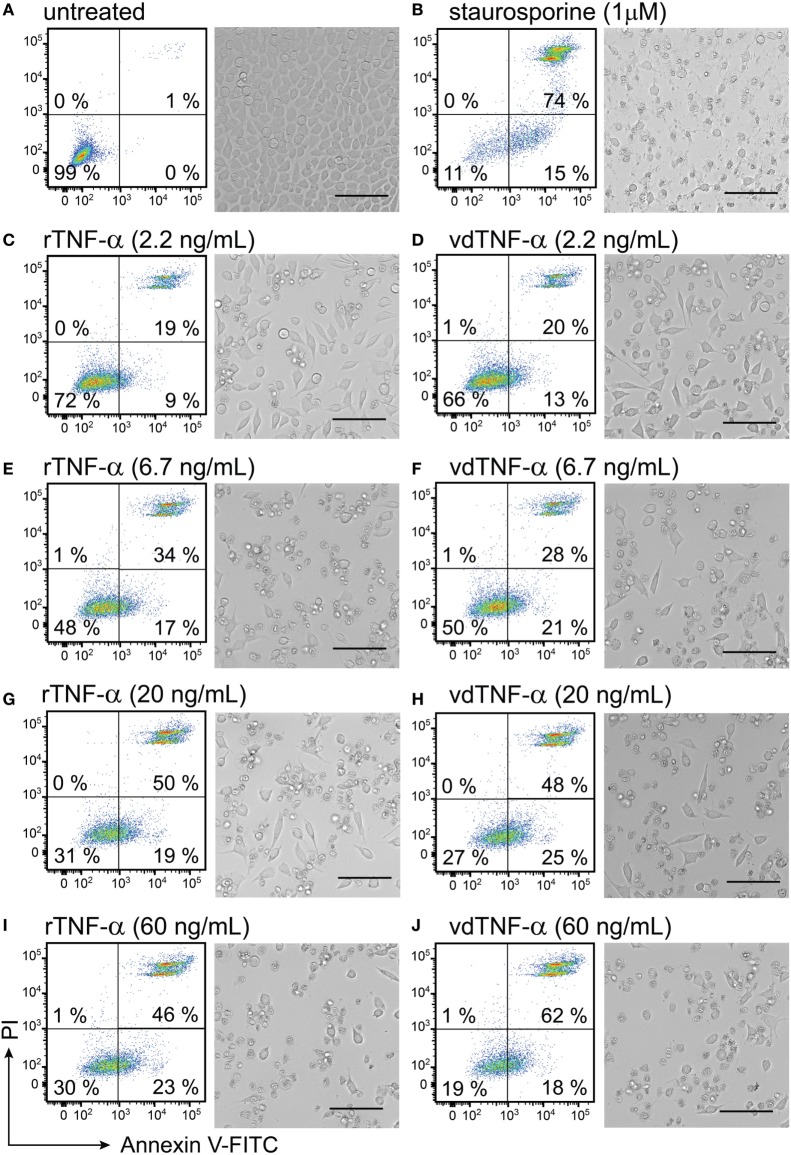
Figure 7.
Vector-derived TNF-α induces cell death in L929 fibroblasts. L929 cells were cultured for 24 h until they reached 90% confluency. The cells were then (A) left untreated for 24 h and used as a negative control or (B) treated with 1 µM staurosporine for 24 h at 37°C and used as a positive control. The remaining cells were treated with rTNF-α or vdTNF-α for 24 h at the following concentrations: (C,D) 2.2 ng/mL, (E,F) 6.7 ng/mL, (G,H) 20 ng/mL or (I,J) 60 ng/mL. The resulting cell monolayers were analyzed using bright-field microscopy (scale bar, 50 µM). Cell death was determined using flow cytometry analysis after cell staining with annexin V-FITC (depicted on the x-axis) and propidium iodide (PI, depicted on the y-axis). Annexin V-positive/PI-negative cells were regarded as apoptotic, whereas annexin V-positive/PI-positive cells were regarded as necrotic. Two independent experiments were performed in duplicates with standard error not exceeding 10% between independent experiments. Data from one representative experiment are shown, where the percentages of the four distinct cell populations represent the averages of duplicates with SEM <10%.