Figure 8.
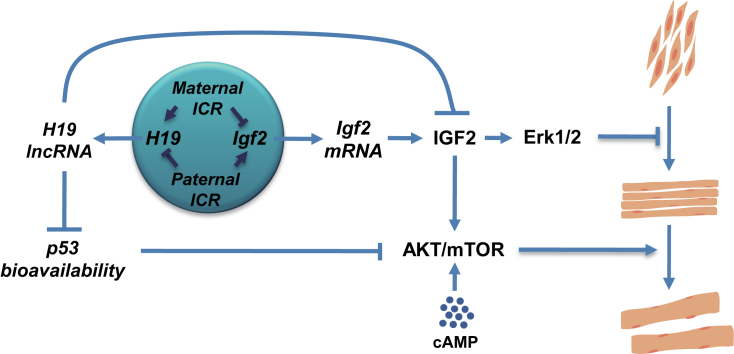
Interactions between H19 and Igf2 regulate muscle cell development. Imprinted expression of H19 and Igf2 genes is determined by the H19ICR. Disruptions in ICR function on the maternal chromosome result in biallelic expression of Igf2 and reduced expression of H19 while disruptions on the paternal chromosome result in reduced expression of Igf2 and biallelic expression of H19. H19 lncRNA directly represses Igf2 RNA levels (63). In addition, H19 is required for normal activation of the AKT/mTOR signaling pathways because H19 lncRNA modulates p53 levels and activity and therefore reduces p53-mediated repression of InsR and Igf1R. Igf2 mRNA encodes IGF2 peptide which activates MAPK signaling through the InsR and Igf1R receptor kinases. MAPK (or Erk1/2) signaling is normally downregulated as myoblasts differentiate into myotubes but excessive IGF2 in LOI cells results in hyperactivation of Erk1/2 and prevents normal differentiation. In addition, IGF2 activates AKT/mTOR signaling. In LOI myoblasts, the loss of H19 and the extra IGF seem to cancel out so that AKT signaling is relatively normal.