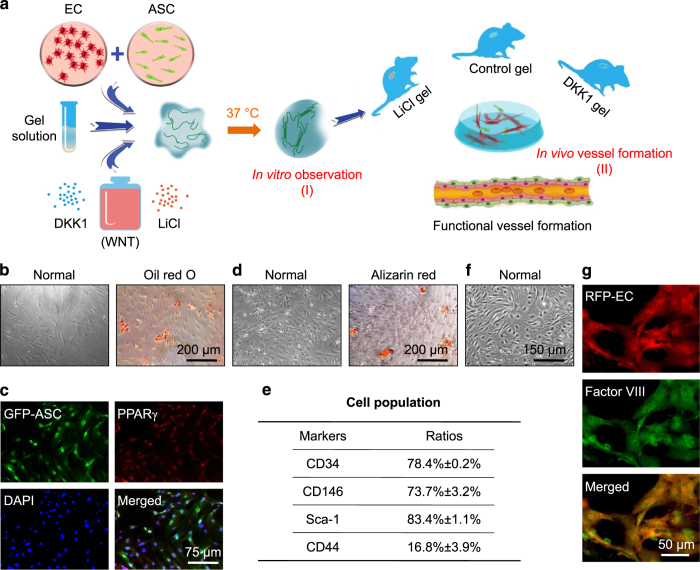
Figure 1.
Experimental protocol and cell identification. (a) Schematic illustration showing total experimental protocol to establish a 3D vascular collagen model in vitro and in vivo. Briefly, GFP-ASCs and RFP-ECs were co-cultured at a 1:1 ratio and suspended in collagen matrices with a Wnt regulator, LiCl, or DKK1, and then gelled at 37 °C and studied in vitro. The gels were implanted into subcutaneous pockets at both dorsal sides of nude mice to set up an in vivo animal model for testing angiogenesis induced by Wnt regulators. Gels were collected and immediately macroscopically imaged by modified CLSM and then sectioned for histological and immunohistochemical analyses. (b–e) Identification of ASCs from mouse fat tissue. Oil Red O (b) and PPARγ (c) show adipogenic differentiation of isolated ASCs, and Alizarin Red (d) shows osteogenic differentiation. The stain images shown are representative of four different experiments (n=4). Flow cytometry (e) showing positive staining for CD34, CD146, and Sca-1 in isolated ASCs (n=3). (f and g) Identification of ECs from mouse brain microvascular tissue. Representative image (f) showing isolated primary ECs, and factor VIII immunofluorescence (g) showing EC marker staining in isolated ECs (n=3).