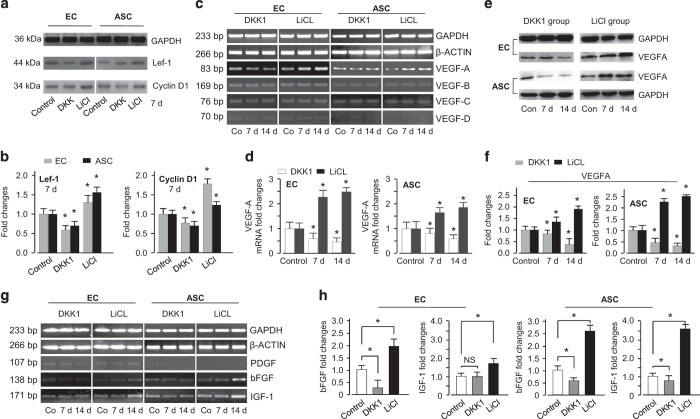
Figure 7.
Nuclear translocation of β-catenin regulates Lef-1 and cyclin D and activates the transcriptional targets of growth factors. (a and b) The expression of Lef-1 and cyclin D regulated by DKK1 and LiCl in ECs and ASCs as shown by western blotting (a) and OD quantification with Quantity One 4.6.3 software (b). The data shown are representative of three different experiments (n=3). *P<0.05. (c–f) Nuclear translocation of β-catenin activates VEGFA expression. (c) Semi-quantitative PCR screened for the gene changes of VEGFA in ECs and ASCs regulated by DKK1 and LiCl. The gels shown are representative of three different experiments (n=3). Quantitative real-time PCR (d) confirmed VEGFA transcriptional changes in both ECs and ASCs. The images are representative of three different experiments (n=3). *P<0.05. Western blot (e) shows the protein expression of VEGFA in ECs and ASCs regulated by DKK1 and LiCl. OD quantification (f) confirmed protein changes (n=3). *P<0.05. (g and h) Nuclear translocation of β-catenin activates gene changes of growth factors, that is, PDGF, bFGF, and IGF-1, by semi-quantitative PCR (g) and quantitative real-time PCR (h). The gels (g) and experiments (h) shown are representative of three different experiments (n=3). *P<0.05.