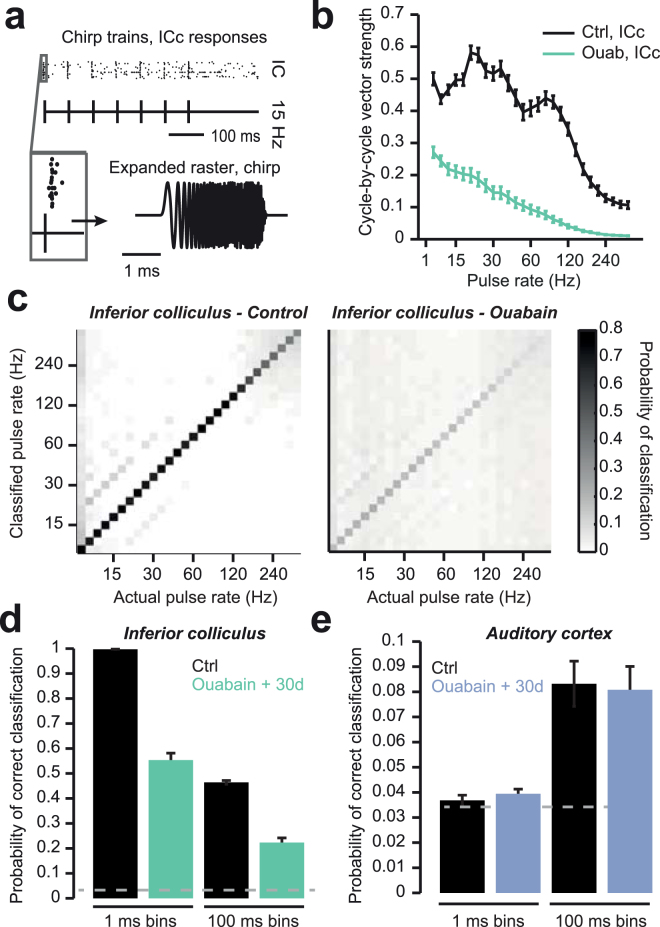
Figure 2.
Auditory nerve damage is associated with profound impairments in auditory temporal processing. (a) Schematic of chirp train stimulus and example raster of IC responses to a 15 Hz pulse train. (b) Vector strength measures the synchronization of the neural response to a temporally modulated stimulus. Synchronization is reduced in the ICc 30 days after ouabain (green line) compared to sham-treated control mice (black line). (c,d) A PSTH-based minimal Euclidean distance classifier (see Methods) was used to classify chirp train frequencies according to multiunit responses. Average confusion matrices (bin size = 10 ms) for control- (left) and ouabain-treated mice (right) show a significant decrease in chirp train classification performance after ouabain that did not recover to control levels with 30 days of recovery in the ICc. Average correct classification in the ICc (c) and ACtx (d) in control- and ouabain-treated mice when using PSTH bin sizes of 1 or 100 ms. Ensembles of 20 units were utilized for the classification analysis. All data in Fig. 2 have been published in an earlier report12.