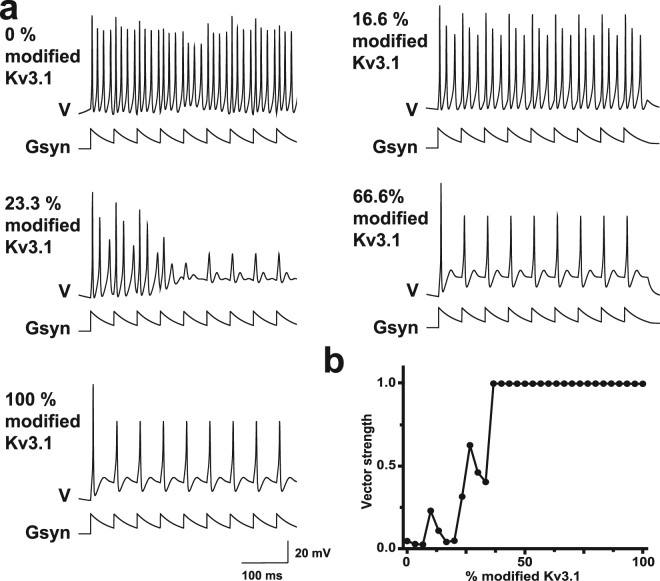
Figure 4.
A numerical simulation suggests that increased Kv3.1 currents improves spike synchronization to periodic synaptic inputs. (a) A simplified computer model based on voltage-dependent Na+ and K+ currents was used to predict firing patterns (V) in response to a 20 Hz train of synaptic inputs (Gsyn). The effects of AUT00063 were simulated by computationally mixing low-threshold current from AUT-modified channels to the normal high-threshold Kv3.1 currents at levels ranging from 0–100%. (b) Precise synchronization to the 20 Hz synaptic input, as estimated from the vector strength statistic, improves with the addition of modified low-threshold Kv3.1 currents.