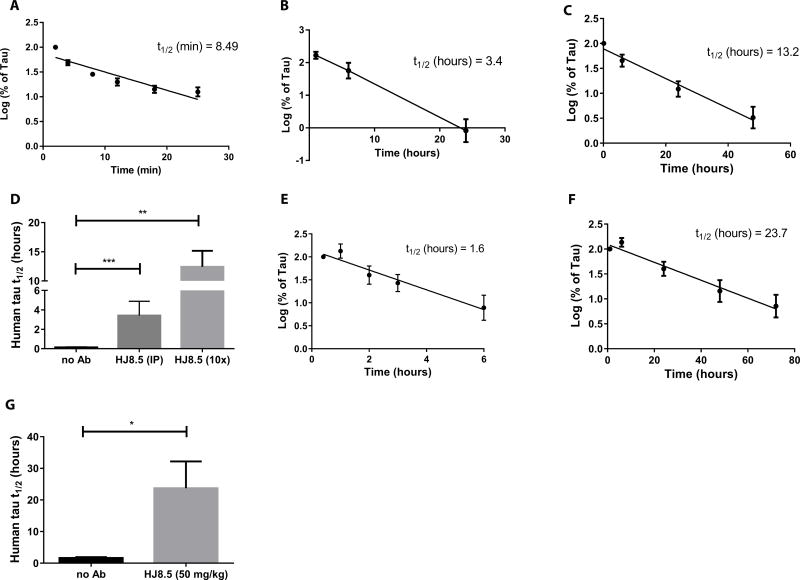
Fig. 2. Half-life of plasma tau in absence and presence of mouse anti-human tau antibody HJ8.5.
(A) Human tau was injected intravenously (i.v.) into wild-type B6C3 mice (n=6) and plasma tau was analyzed at 2, 4, 8, 12, 18 and 25 minutes (min). (B) Human tau was injected i.v. into wildtype B6C3 mice (n=9) 1 hour following i.p. administration of humanized anti-tau antibody HJ8.5 at 50 mg/kg and plasma tau was analyzed after 30 minutes, 6 hours, and 24 hours. (C) Human tau was pre-incubated for 1 hour with 10× molar excess of HJ8.5 and injected into the jugular vein of wildtype mice (n=8). Plasma was collected at 10 minutes, and 6, 24, 48, and 72 hours. (D) Half-life of plasma tau following jugular vein injection of human tau under the conditions studied in A, B, and C. (E) Human tau was injected into the cisterna magna of wildtype B6C3 mice (n=6) and plasma was collected at 25 minutes, and 1, 2, 3, and 6 hours. (F) Ten minutes after HJ8.5 antibody injection (50 mg/kg, i.p.), human tau was injected into the cisterna magna of wildtype mice (n=6) and plasma was collected at 10 minutes, and 1, 6, 24, 48, and 72 hours. (G) Half-life of plasma tau after injection into the cisterna magna of wildtype mice in the absence (E) and presence of HJ8.5 (F). Tau half-life was calculated by determining the slope from linear regression fit of semi-log plots of concentration versus time (41). Values in D and G represent mean ± SEM. *p≤0.05, **p≤0.01, ***p≤0.001. Values in D analyzed by ANOVA followed by post-hoc Dunnett’s test and values in G analyzed by unpaired t test.