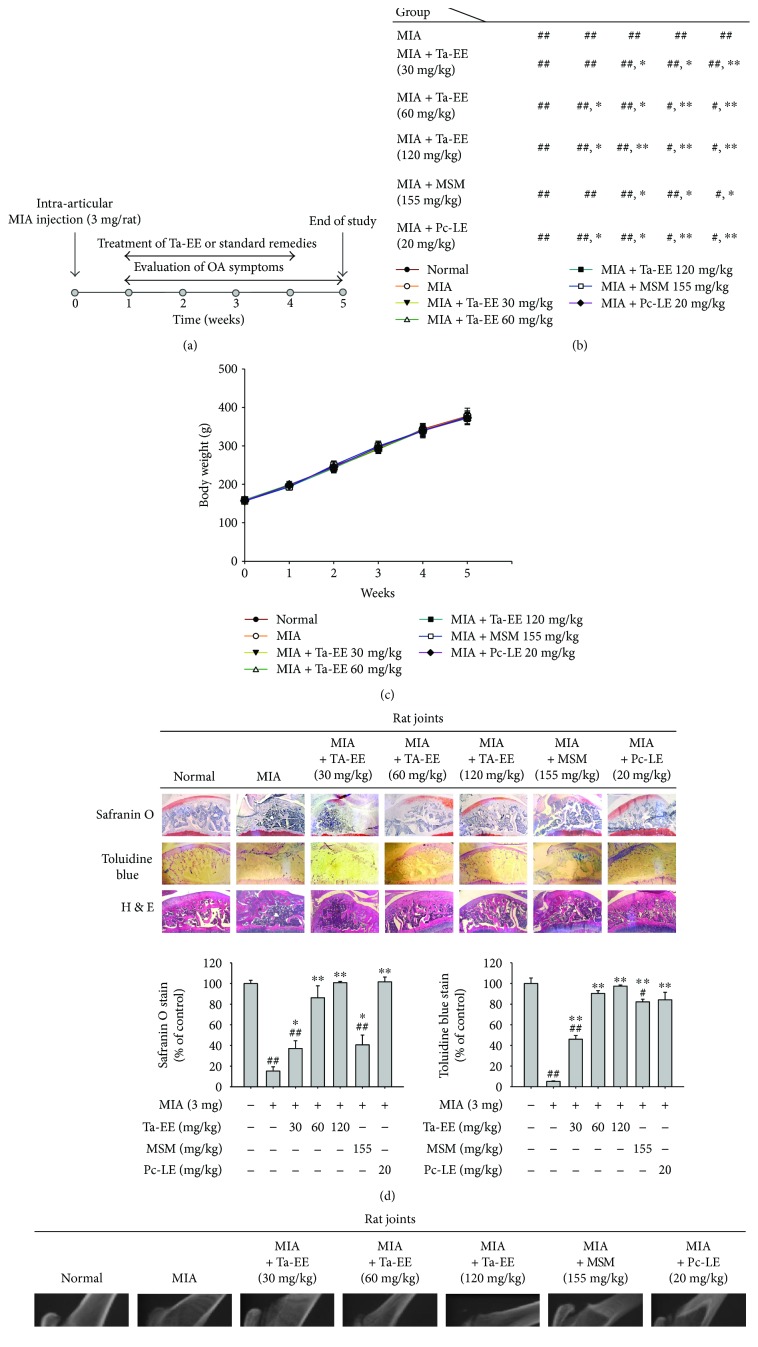
Figure 1.
Ta-EE ameliorated OA symptoms in MIA-induced OA rats. (a) Experimental schedule of OA induction, treatment, and evaluation. Sprague-Dawley rats (10 rats/group) were intra-articularly injected with MIA (3 mg/rat). One week later, the rats were subjected to different treatments once a day for four weeks. The study finished at week five. (b) MIA-induced OA rats were orally administered with either Ta-EE (30–120 mg/kg), MSM (155 mg/kg), or Pc-LE (20 mg/kg) once a day for four weeks, and paw withdrawal threshold was measured once a week for five weeks. The significance of each group with respect to the MIA group each week is summarized in the box. (c) Body weights of the rats were measured once a week for five weeks. ((d); left panel) MIA-induced OA rats were orally administered with Ta-EE (30–120 mg/kg), MSM (155 mg/kg), or Pc-LE (20 mg/kg) once a day for four weeks, and the tibia bones were stained with hematoxylin and eosin, safranin O, or toluidine blue at week five. The areas stained by ((d); middle panel) safranin O and ((d); right panel) toluidine blue were measured and plotted. (e) The femur and tibia bones of the MIA-induced OA rats administered with Ta-EE (30–120 mg/kg), MSM (155 mg/kg), or Pc-LE (20 mg/kg) were analyzed by X-ray radiography. ∗P < 0.05 and ∗∗P < 0.005 versus a control group; #P < 0.05 and ##P < 0.005 versus a normal group.