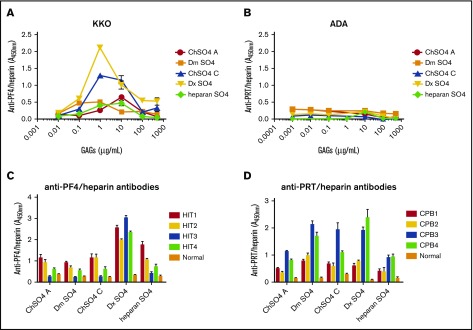
Figure 3.
Binding of antibodies to PF4/GAGs or PRT/GAGs. (A) Binding of KKO to PF4/GAGs. KKO 2 ng/mL was incubated with microtiter wells coated with PF4 alone or with PF4/GAG complexes containing increasing concentrations (1 ng/mL to 500 µg/mL) of chondroitin sulfate (ChSO4 A or ChSO4 C), dermatan sulfate (Dm SO4), dextran sulfate (Dx SO4), or heparan sulfate (heparan SO4). (B) Binding of ADA to PRT/GAGs. Similar studies as shown in (A) were performed using ADA 50 ng/mL and wells coated with PRT or PRT/GAG complexes (1 ng/mL to 500 µg/mL). (C) Binding of HIT antibodies to PF4/GAGs. Patient-derived HIT antibodies (HIT1-4) or normal plasma were diluted 1:100 in wells coated with PF4/GAG complexes. Antibody binding to PF4/GAG 10 µg/mL is depicted. (D) Binding of PRT/heparin antibodies to PRT/GAGs. Patient-derived PRT/heparin antibody samples (CPB1-4) or normal plasma were diluted 1:2000 in wells coated with PRT/GAG complexes. Antibody binding to PRT/GAG 10 µg/mL is depicted. Polyclonal PRT/heparin antibodies displayed differential binding to PRT/GAG complexes. All data shown are representative of 3 independent determinations.