Fig. 1.
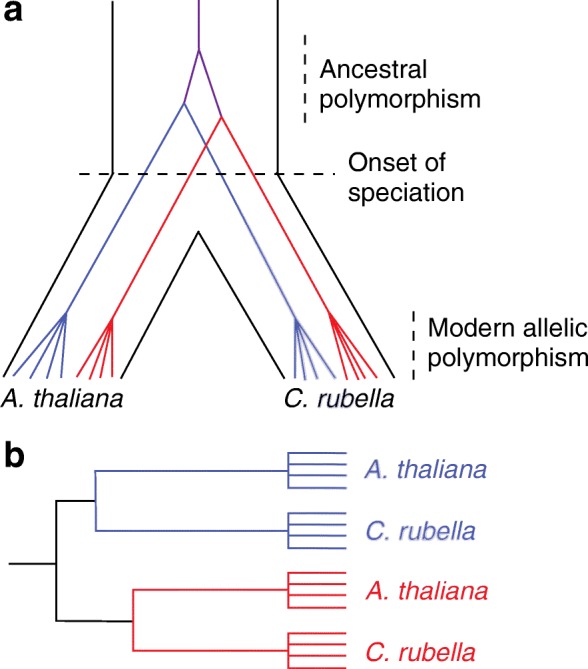
Origin and identification of trans-specific polymorphisms at a single-copy locus. a Time runs from top to bottom, and variation within a species is enclosed by flanking black lines. Before the onset of speciation, two alleles segregate within the ancestral species (purple lines), and each copy gives rise to a pair of descendant alleles (two blue or two red). As speciation proceeds, these descendant alleles are inherited in the daughter species, and finally modern allelic polymorphism exists among individuals. (As is typical in coalescent analyses, only lineages that are represented in our modern sample are shown.) b An allele phylogeny showing the relationships of modern, sequenced alleles at one single-copy gene. In the blue clade, Arabidopsis thaliana alleles are more closely related to blue alleles in Capsella rubella than to red alleles in A. thaliana because of trans-specific polymorphism. Figure adapted from Wu et al. [1]
