Figure 1. Schematic representation of various proteins associated with CAG-disorders.
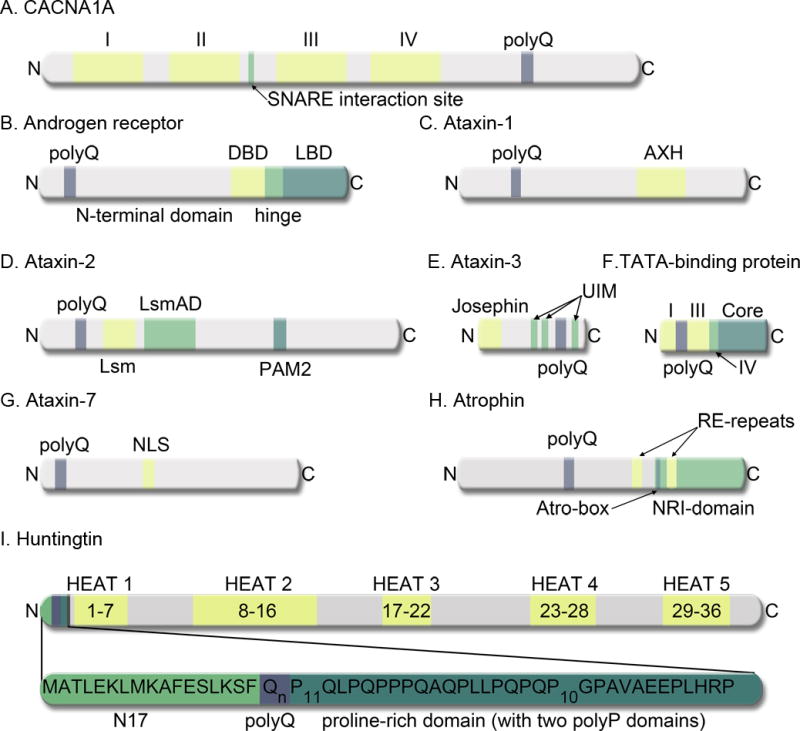
A, CACNA1A, in addition to the polyQ tract, contains four homologous domains (I–IV), each with six transmembrane segments. There is a SNARE interacting site between domains II and III. B, Androgen receptor, in addition to the polyQ tract, contains an N-terminal domain (NTD), a DNA-binding domain (DBD), a hinge region, and a ligand-binding domain (LBD). C, Ataxin-1 contains a polyQ tract and an AXH domain. D, Ataxin-2, contains the polyQ domain, a Like RNA splicing domain Sm1 and Sm2 (Lsm), a Like-Sm-associated domain (LsmAD), and a poly (A)-binding protein interacting motif 2 (PAM2). E, Ataxin-3 contains an N-terminal Josephin domain, three Ub-interacting motifs (UIM), and the polyQ domain. F, The N-terminal region of the Tata-box binding protein consists of four domains (I-IV) followed by a core region. The polyQ region is domain II. G, Ataxin-7 contains a polyQ domain and a putative nuclear localization signal (NLS). H, Atrophin-1, in addition to the polyQ tract, contains two arginine-glutamic acid dipeptide repeats (RE repeats), a nuclear receptor interacting domain (NRI domain), and a highly conserved Atro-box domain. I, The full-length htt protein contains several HEAT repeats. The inset indicates the location of htt exon1, with the N17, polyQ, and proline-rich domains indicated.
