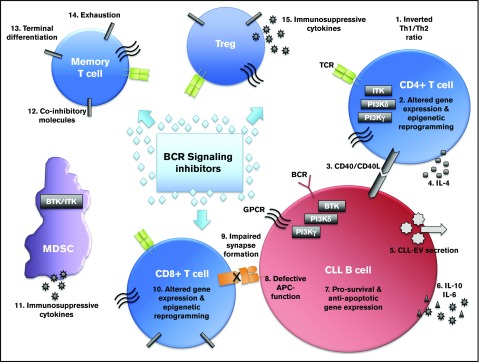
Figure 1.
The complex interplay of immune subsets in chronic lymphocytic leukemia that may be affected by B-cell receptor signaling inhibitors. BCR signaling inhibitors, such as ibrutinib, idelalisib, and others, act directly on the malignant B cell. However, recent research demonstrates that BCR inhibitors act on various immune cell types within the CLL microenvironment that control immune dysfunction and immune-related serious adverse events occurring in patients. Novel mechanisms of action for B-cell receptor inhibitors characterized in these immune cells may lead to repurposing of the drug for use in other cancers or autoimmune conditions.