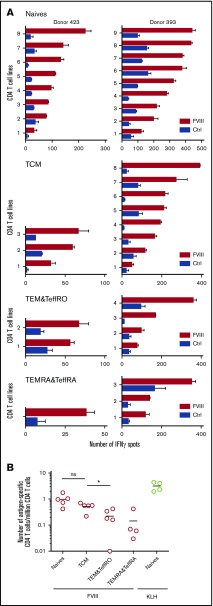
Figure 2.
Characterization of FVIII-specific CD4 T-cell subsets. CD4 T cells were separated by flow cytometry into 4 subsets: naïve T cells (CD45RA+ CD45RO− CD127+ CD62L+ CD197+), central memory cells (TCMs; CD45RA− CD45RO+ CD127+ CD62L+ CD197+), effector memory cells and effector cells CD45RO+ (TEM&TeffRO; CD45RA− CD45RO+ CD127+ CD62L−), and effector memory cells and effector cells CD45RA+ (TEMRA&TeffRA; CD45RA+ CD45RO− CD127+ CD62L−; supplemental Figure 1). CD4 T-cell lines were generated from the cells of these subsets by 3 once-per-week rounds of in vitro stimulation with autologous DCs loaded with 0.2 µM of FVIII or 0.25 µM of KLH (for naïve cells only). Specificity of CD4 T-cell lines raised against FVIII or KLH was analyzed by IFN-γ ELISPOT. (A) FVIII-specific T-cell lines obtained from the different CD4 T-cell subsets isolated from 2 representative donors: #393 and #423. (B) Frequencies of FVIII-specific CD4 T cells isolated from the different CD4 T-cell subsets of all donors. Statistical significance was assessed using the Wilcoxon match-pairs signed rank test. *P < .05. Ctrl, control.