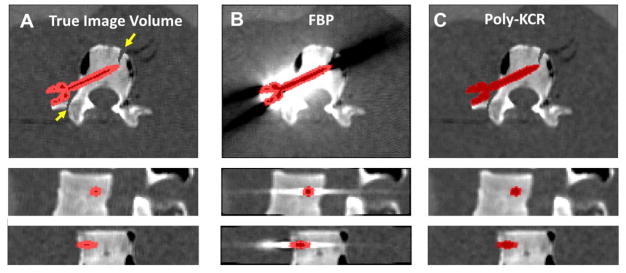
Figure 3.
Reconstructions of digital phantom data that includes one pedicle screw with a priori unknown material properties. A) The ground truth image volume with the screw shown as a red color overlay. Simulated fractures are indicated by the yellow arrows. B) FBP reconstruction of the digital phantom shows prominent metal artifacts arising from energy-dependent effects and photon starvation. These artifacts obscure anatomy near the screw including the simulated fractures. C) The Poly-KCR approach effectively uses the shape of the known component to greatly improve image quality. Artifacts and noise are largely mitigated permitting good visualization near the boundary of the screw implant and the background anatomy.