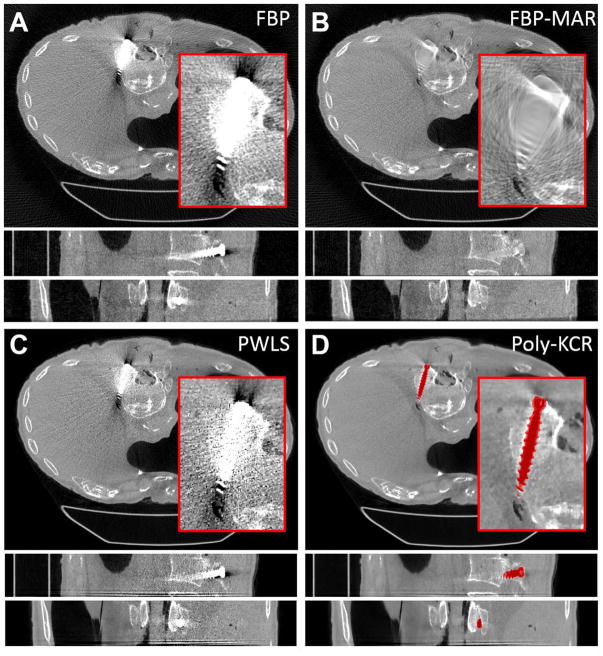
Figure 8.
Reconstructions from the cadaver torso investigations. For each method a zoomed region-of-interest is shown in the axial slice. The grayscale is linear for all images from 0.018 mm−1 to 0.028 mm−1. A) FBP reconstruction exhibited substantial metal artifacts around the pedicle screw. Streaks and increased noise prevent good visualization of the pedicle screw placement within the vertebral body. B) FBP-MAR shows a significant reduction in “blooming” artifacts; however, data interpolation has obscured many features in the vicinity of the pedicle screw. C) PWLS reconstruction shows a slight improvement over FBP but significant artifacts remain. D) The Poly-KCR approach yielded substantial reductions in artifacts largely eliminating blooming and streaking effects. Relatively small residual artifacts can be seen at the head of the screw. However, image quality in the vicinity of the implant is good showing bone details, an air bubble near the tip of the implant, and the lateral breach in the body of the vertebra is easily seen suggesting a potentially significant improvement in diagnostic quality.