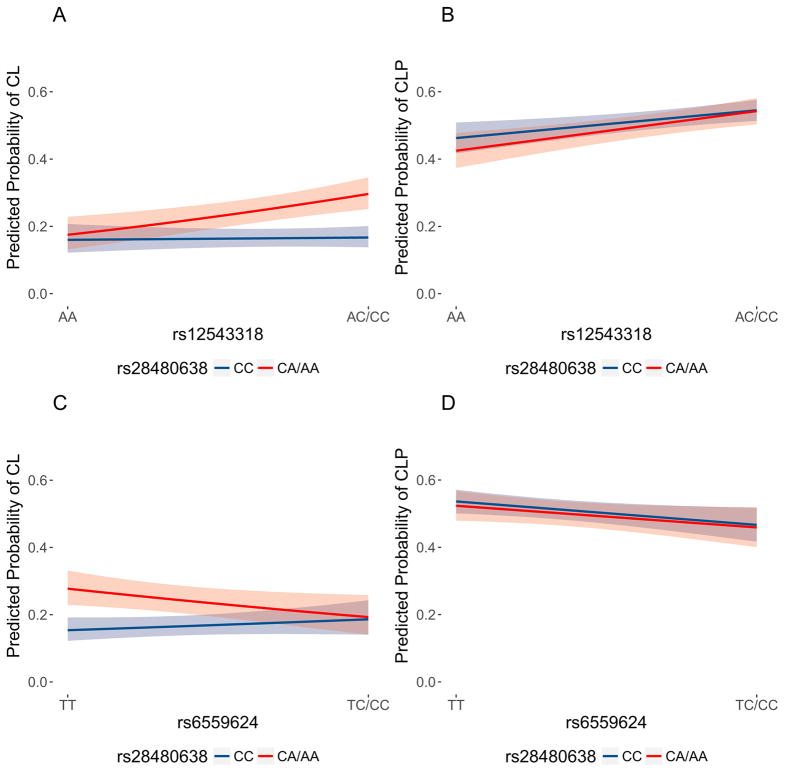
Figure 3.
(A) Predicted probabilities and 95% confidence bands of cleft lip for genotypes of the 8q21 variant, rs12543318, and the 16q21 modifier variant, rs28480638. (B) Predicted probabilities and 95% confidence bands of cleft lip and palate (CLP) for genotypes of the 8q21 variant, rs12543318, and the 16q21 modifier variant, rs28480638. (C) Predicted probabilities and 95% confidence bands of cleft lip for genotypes of the FOXE1 variant, rs6559624, and the 16q21 modifier variant, rs28480638. (D) Predicted probabilities and 95% confidence bands of cleft lip and palate (CLP) for genotypes of the FOXE1 variant, rs6559624, and the 16q21 modifier variant, rs28480638. Predicted probabilities were calculated using the gene-gene interaction models, holding the 18 principal components of ancestry constant at their average values. In each plot, the predicted probabilities for AC/CC genotypes at rs28480638 (which are associated with increased risk of cleft lip) are shaded in red, and those for AA genotypes at rs28480638 are shaded in blue.