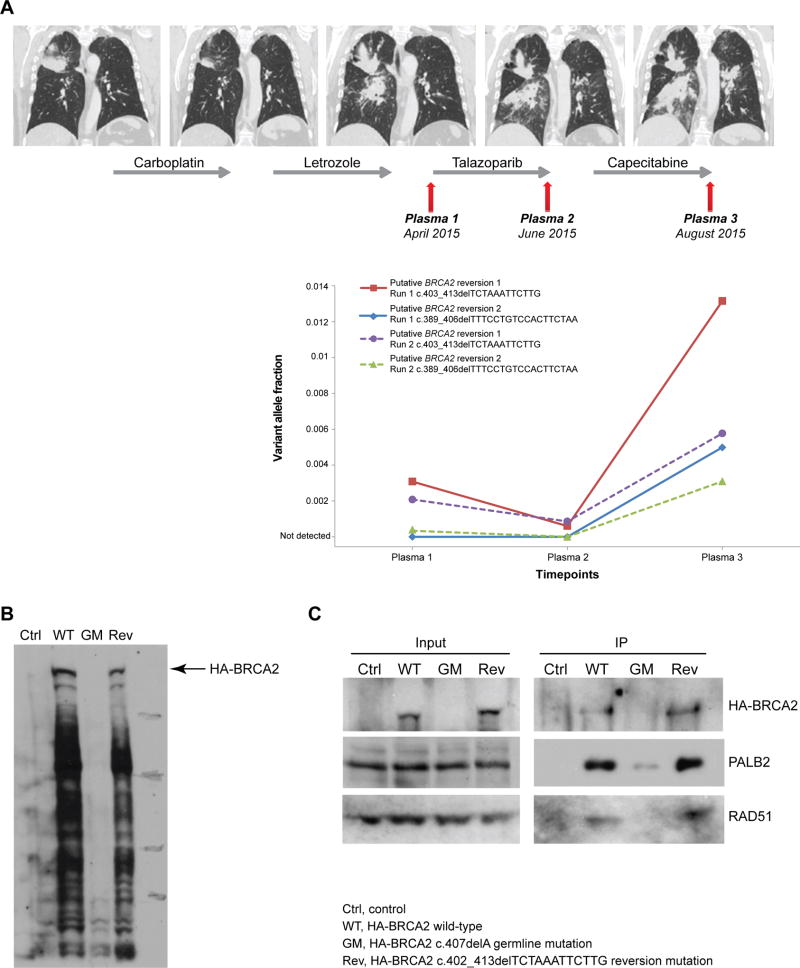
Figure 4. Serial analysis of putative BRCA2 reversion mutations in cfDNA samples from breast cancer patient L031, and the interaction between reversion-mutant BRCA2, PALB2 and RAD51.
A, CT images during the course of therapy of breast cancer patient L031 demonstrating the initial response and subsequent progression of the lesions. Plasma samples were obtained before and after treatment with the PARP inhibitor Talazoparib and after Capecitabine therapy (top). Mutant allele frequencies of two somatic BRCA2 reversion mutations identified by targeted massively parallel sequencing were assessed in two independent analyses in the plasma samples pre- and post PARP inhibitor treatment using targeted amplicon sequencing. B, 293T cells transfected with HA-BRCA2 wild-type (WT), HA-BRCA2 c.407delA germline mutant (GM) and HA-BRCA2 c.402_413delTCTAAATTCTTG somatic reversion-mutant plasmids Rev). Western blot performed using an anti-HA antibody revealed that the HA-BRCA2Rev was translated into mutant protein (predicted 3414AA) with a molecular weight similar to that of the wild-type protein (3418AA). The HA-BRCA2GM protein length is predicted to be 150AA. Immunoprecipitation of HA-BRCA2Rev and wild-type HA-BRCA2 revealed that HA-BRCA2Rev protein displays proficient interactions with PALB2 and RAD51 similar to that of the wild-type BRCA2 protein. AA, amino acid.